Database Systems Basics
ITE2038 Database Systems
Contents
- Relational Model + Schema
- Declarative Queries
- Query Optimization
- Efficient access and updates to data
- Recoverability
- Consistency
What is a database?
- structured data collection
- Records
- Relationships
DB가 다루는 데이터: entity와 그것의 관게 정의되어 있는 것
data 넣고, 사람들이 질문하면 응답 빠르고 정확하게 주는것이 DBMS의 목적.
- MAPD (massively parallel database)
- 대량 data 있을 때 빨리 처리하는 GPU base DB
big data의 real-time querying & visualization을 위해 GPU 사용
(디테일 생략)
Zoo data
추후에 예시로 종종 사용예정
Zoo website features
- Admin interfac
- Edit
- Add an animal
- Public
- Pictures & Maps
- Zookeeper
- Feed times
entity relationship diagram
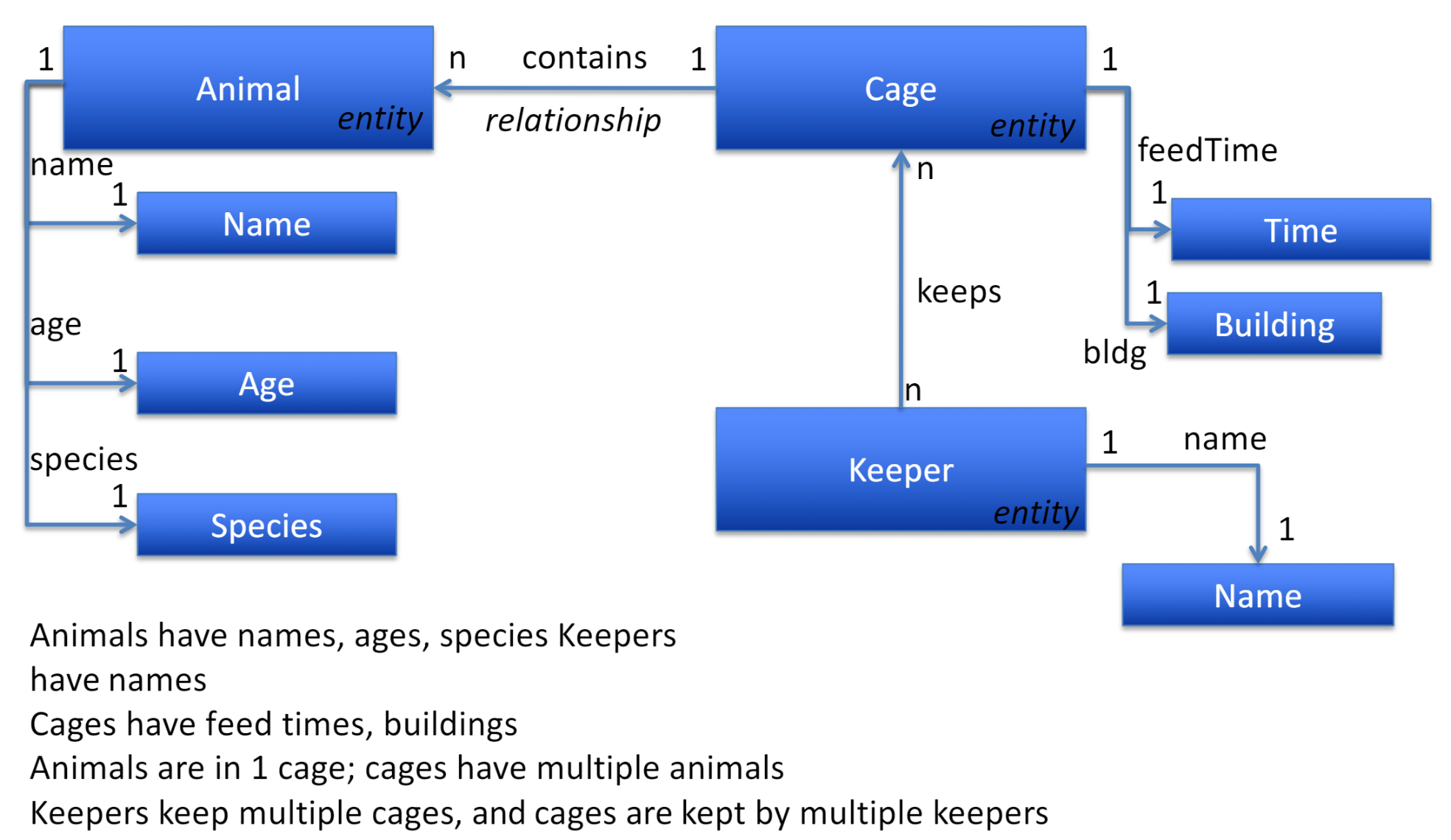
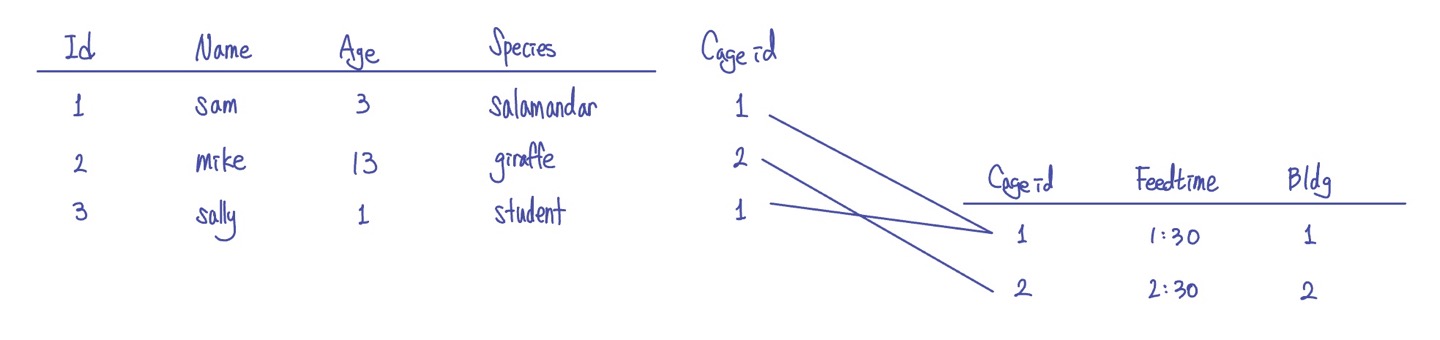 두 table 사이의 relation Cageid로 표현
두 table 사이의 relation Cageid로 표현
relation조차 entity로 표현 (foreign key로 연결)
더 고전적인 relation 나타내는 방법
Hierarchy & Graph
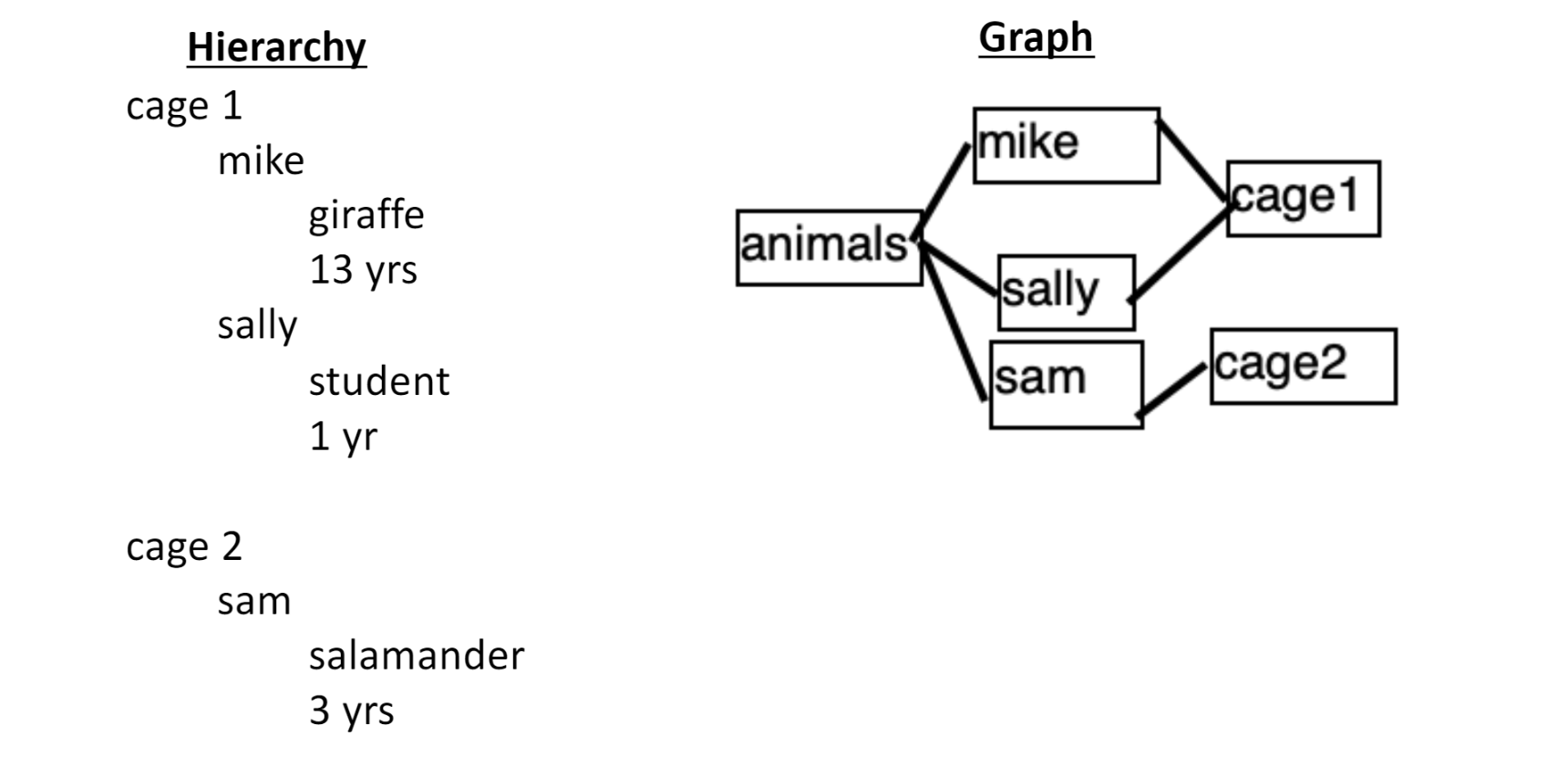
data 정규화 하는 이유: 중복 최대한 피하고자
(추후에 다룸)
SQL - Structured Query Language
: 질의를 하는 언어
가장 기본적인 format:
SELECT field1, ... ,fieldM
FROM table1, ... -- 읽어올 대상이 되는 table
WHERE condition1, ...
값 추가:
INSERT INTO table VALUES (field1, ...)
-> 괄호 안이 값
ex)
insert into keeper values (1,'Jenny');
insert into keeper values (2, 'Joe);
값 수정:
UPDATE table SET field1 = x, ...
WHERE condition1, ...
Declarative Queries
- imparative VS declarative
- Imparative = 명령적, 절차적
C, Java, Python 등. 시키는 것만 함
(nested loops)for each row r in animals if r.species = 'giraffe' output r.name - Declarative = 선언적
how X, what O
어떻게 해야하는지 명시 X, 뭘 해야하는지만 명시 O
(join)
SELECT r.name FROM animals WHERE r.species = 'giraffe' - Imparative = 명령적, 절차적
- 코드로 비교
- 종이 기린인 모든 동물의 이름 출력
- Imparatives
for each row r in 'animals' if r.species = 'giraffe' output r.name - Declarative
SELECT r.name FROM animals WHERE r.species = 'giraffe'
- Imparatives
- Building32의 모든 cage
- Imparative
for each row a in animals for each row c in cages if a.cageno = c.no and c.bldg = 32 output a - Declarative
SELECT a.name FROM animals AS a, cages AS c WHERE a.cageno = c.no AND c.bldg = 32
- Imparative
- 종이 기린인 모든 동물의 이름 출력
Query examples
- 곰 나이의 평균
SELECT AVG(age) FROM animals WHERE species = 'bear'<Complex Queries>
- 한살 이상의, 같은 종의 암수의 쌍 출력
SELECT a1.name, a2.name -- 4) 한 쌍 FROM animals as a1, animals as a2 WHERE a1.gender = M and a2.gender = F -- 3) 암수 AND a1.species = a2.species -- 2) 종이 동일한 AND a1.age>1 and a2.age>1 -- 1) 1살 이상인=> self join
animal table은 1개인데, 2개인것처럼 연결하는 것 - 평균적으로 밥 먹는 (feed time)시간보다 늦는 salamander 종인 동물
SELECT cages.cageid FROM cages, animals
WHERE animals.species = 'salamander'
AND animals.cageid = cages.cageid
AND cages.feedtime>
(SELECT AVG(feedtime) FROM cages)
=> nested queries 한 테이블에 결과 추린 후 그 table에 다시 질문한 것
- student와 salamander를 동시에 관리하는 keeper
SELECT keeper.name FROM keeper, cages as c1, cages as c2, keeps as k1, keeps as k2, animals as a1, animals as a2 WHERE c1.cageid = k1.cageid AND keeper.keeperid = k1.keeperid AND c2.cageid = k2.cageid AND keeper.keeperid = k2.keeperid AND a1.sepcies = 'student' AND a2.species = 'salamander' AND c1.cageid = a1.cageid AND c2.cageid = a2.cageid
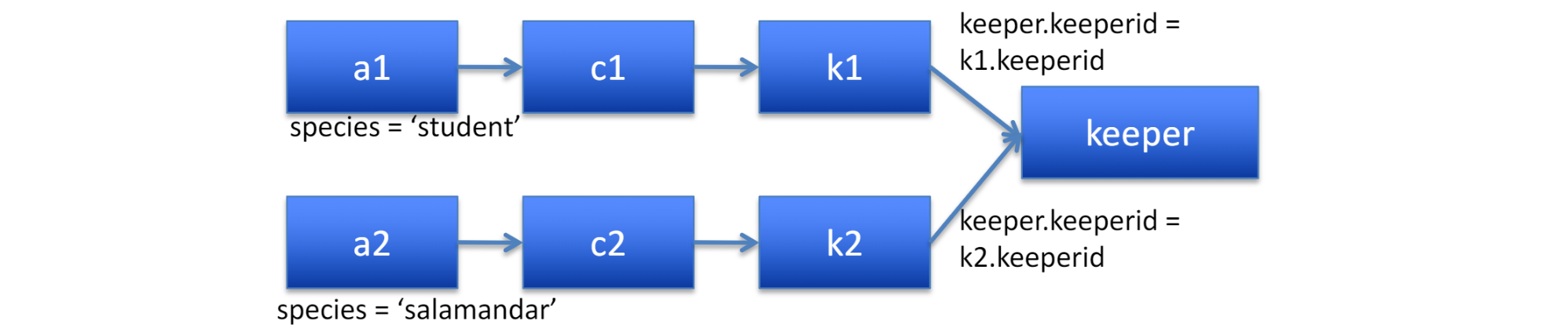
동물은 어떤 cage에 살꺼고, -> 그 cage의 사육사 id 있을 꺼고, -> 이 ID 들이 같은 경우 출력
Declarative Queries
: ‘What’ not ‘How’

SQL -> Procedural Plan -> Optimized Plan -> Compiled Program
SQL 쿼리에 대한 여러 후보 plan (Procedual Plan)
처리하는 데이터 양이 적거나 횟수가 적은 등 **제일 비용 적은** plan (Optimized plan)선택
optimized plan의 예시로, WHERE 뒤에 들어가는 condition
join 후에 condition 들어가는 것이 아닌,
condition 먼저 선별 수 join
출처 : 2023-2 ITE2038 수업