Relational DB
ITE2038 Database Systems
Key ideas :
Relational vs Other Data Models
Advanced SQL
Contents:
- Data models + history
- Hierarchical (IMS/DL1) - 1960’s
- Network (CODASYL) - 1970’s
(그래프 DB) - Relational - 1970’s and beyond
- Key ideas
- Data redundancy(and how to avoid it)
- Physical and logical data independence
- Relational algebra and axioms
(수학처럼 계산 가능(실용적))
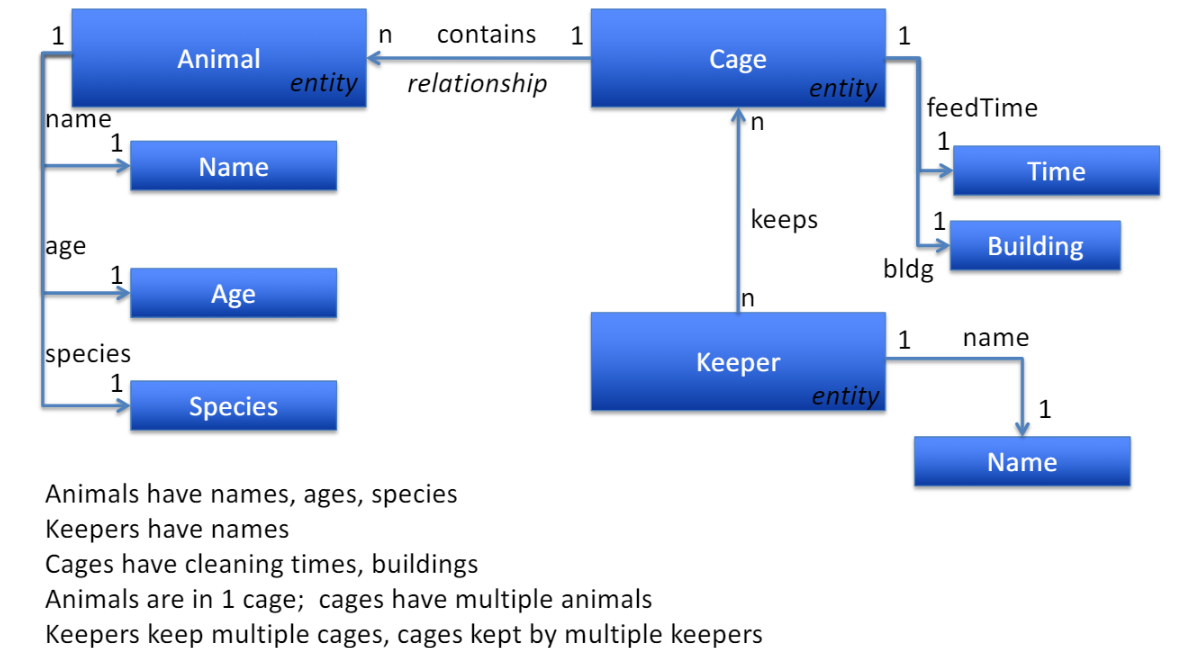
Zoo data model
Entity Relationship Diagram
Zoo tables
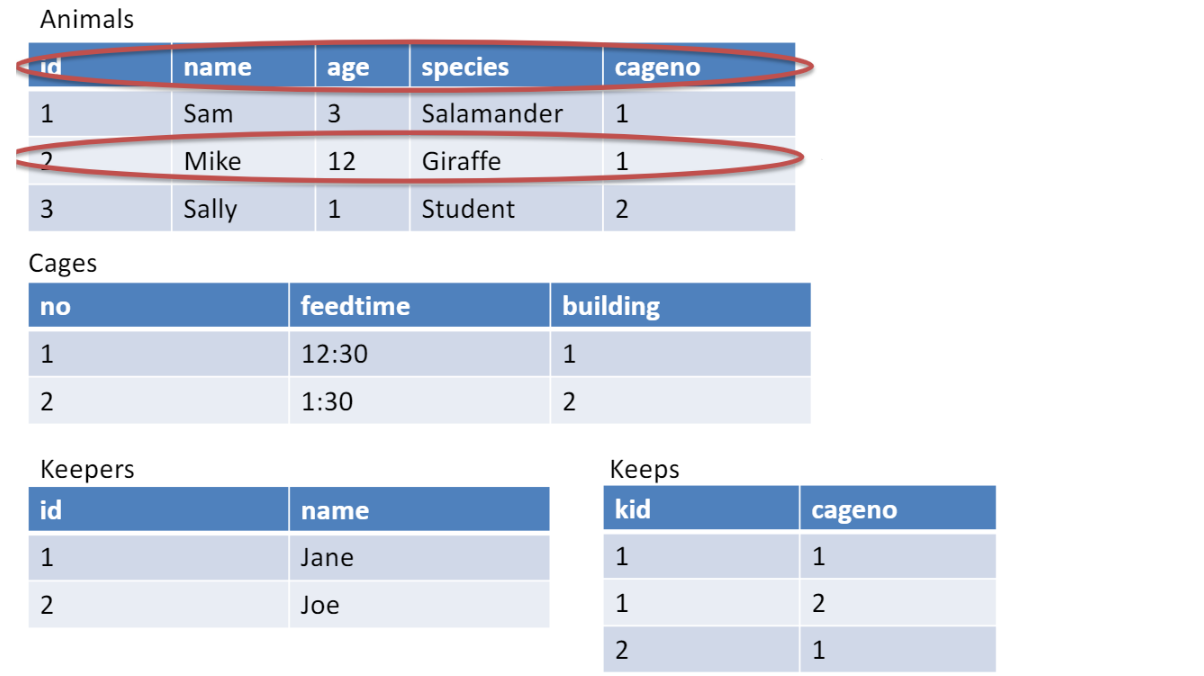
-
Schema
Field names & types -
Rows = records = tuples
-
Primary key⭐
테이블에서 각 레코드를 unique 하게 구분하기 위한 것
(위 table에서 id, no등이 해당) -
Foreign key⭐
다른테이블의 레코드와 연결 위한 것
(animal table의 cageno 통해 cages table 연결)
Primary key, foreign key 사용해서 하나의 table인 것 처럼 표현
attribute 통해서 relation 표현
Modified Zoo data model
지난 post에서는 한 cage에 한 animal만 있었지만, 한 cage에 여러 동물.
한 animal 당 한 keeper있었지만, keeper들은 여러 동물 care함.
=> 기존방식 문제됨.
-
한 cage에 여러 동물 있을 때 animal table에서 cage 정보 여러번 써지는 것
-
새로운 사육사 왔는데 배정된 animal 없는 경우, DB 작성 불가
IMS(Hierarchical Model)
- Data들이 segment로 정리
- 같은 segment 타입인 레코드들의 collection.
- segment들이 tree처럼 정렬
Keepers ㄴ Animals ㄴ Cages
- Segment들은 각각 다른 물리적 representation 가짐.
물리적 저장방법 지정 가능- unordered / indexed (sorted,hashed) 등 지정 가능
example hierarchy

physicalrepresentation
A1 Segment A2 Segment A3 Segment
C1 Segment C2 Segment C3 Segment
-> segment의 선택이 적용될 operation에 영향
Operation example
-
GetUnique(seg type, pred): pred를 만족하는 첫 레코드 get
-
GetNext(seg type, pred): hierarchical order에서, 첫번째나 다음 key 얻음
(… 디테일 생략) #10
단점
- hierarchical 데이터가 아닌 경우, 데이터의 중복 발생
- low level programming 인터페이스 (Search 알고리즘 코드 짜야함)
- 제한적인 physical data independence
- root를 keeper에서 animals로 변결 -> 불가
- root를 indexed에서 hash로 변결 -> 불가
- 제한적인 logical data independence
- 스키마가 변경되면, 프로그램도 변경되어야함
CODASYL
(Conference/Committee on Data Systems Languages)
1) 데이터의 중복이 심하다 2) 물리적으로 저장되는 형태 지정되어 유지보수 측면에서 불리
위 문제점을 해결하고자 고안한 방법
-> Graph or network-based data model 고안
entry point 찾고, multidimensional space 에서 navigate around 하는 방법으로 데이터 탐색
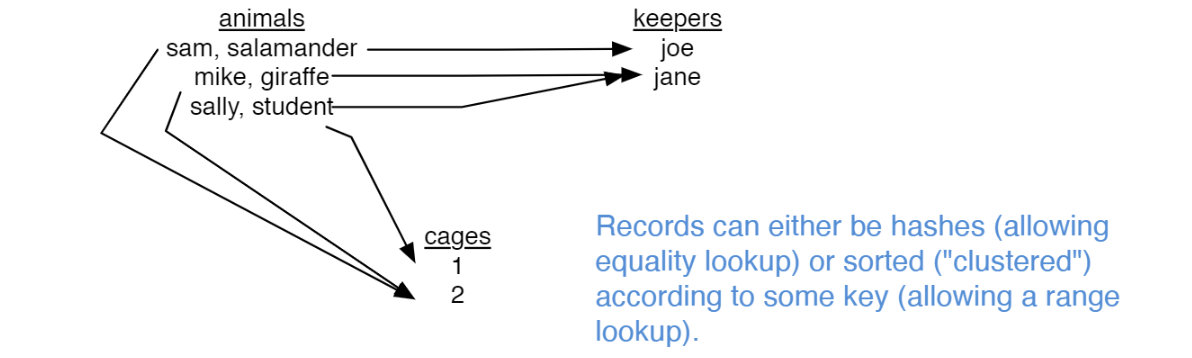
단점
- “Navigational Programming” 매우 complex
- 여전히 physical, logical data independence 부족 해결 못함
- 프로그램 수정 없이 스키마 변경 불가
- 다른 인덱스 타입이 다른 operation 지원 할수도 안할수도 있기에, physical representation 변경 불가
-> 이것 개선 하는 Relational model
Relational model
Relational Principls (원칙)⭐
- 단순한 representation(tree, graph는 다루기 깔끕하고 쉬운 구조 X)
- 집합으로 생각해 중복 X, 길고 복잡한 네비게이션 필요 X
- 물리적 데이터 모델 description 필요 없음
Relational Data Model⭐
- 모든 데이터는 record(tuple)들의 table로 표현 됨.
- Table은 unordered set(중복 X)
- DB는 한개 이상의 table로 구성
- 각 relation은 column의 type을 기술하는 schema(data type 정해주고, key들로 table간의 relation 지정해준 것)있다.
- 각 field는 primitive type – set 또는 relation이 아님
Primitive라는 것
이용가능한 가장 단순한 요소. 원자 atom 처럼 가장 작은 단위를 의미
cf. 덧셈, 뺄셈같이 가장 단순하고 원초적인 연산을 primitive operation이라고 하기도 함 https://powerofsummary.tistory.com/251 - 데이터의 물리적(physical) representation은 구체화(specify) 되지 X
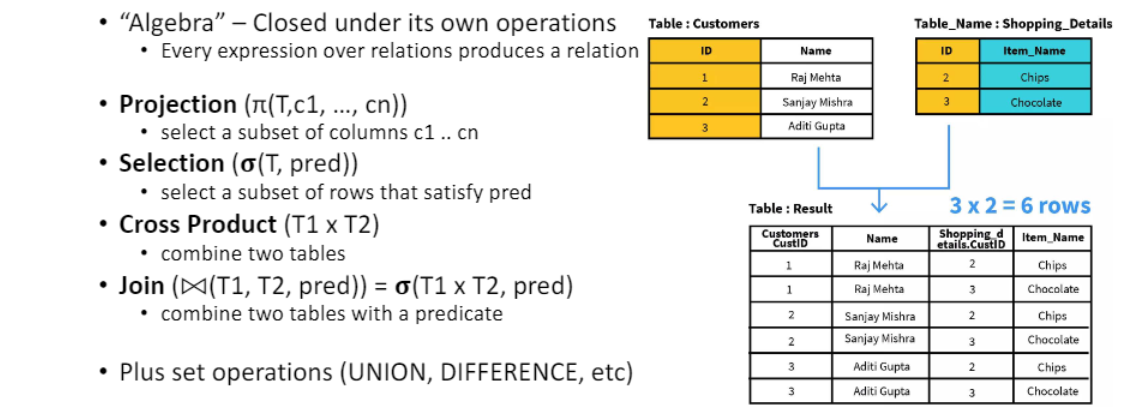
Relational Algebra ⭐
-
Projection (π(T,c1, …, cn))
column의 subset c1 .. cn 선택
수직 분할 -
Selection (σ(T, pred))
pred를 만족하는 row의 subset 선택 -
Cross Product (T1 x T2)
두 table 결합 -
Join(⨝(T1, T2, pred)) = σ(T1 x T2, pred)
predicate으로 두 table 결합 -
Plus set operations (UNION, DIFFERENCE, etc)
•“Algebra” –Closed under its own operations
Every expression over relations produces a relation
정리본 참고하기
https://dad-rock.tistory.com/382
Relational Identities

Join Ordering Example
Joe가 관리하는 building 찾기
SQL:
SELECT building
FROM cages JOIN keeps ON no = cageno
JOIN keepers on kid = id
WHERE name = ‘Joe’
위의 SQL을 수행 하는 두 방법 예시:
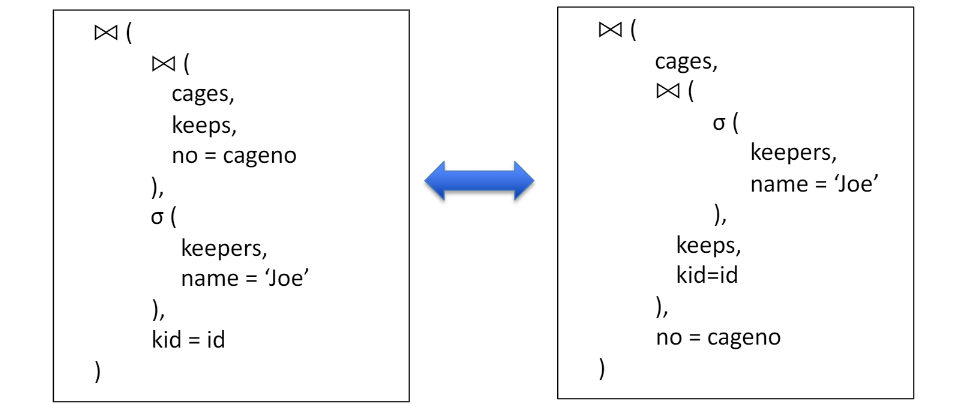
-
최적의 ordering은 table의 size에 따라 다름
-
다만 대부분의 경우, 선택(select) 후 join이
join 후 선택하는 것 보다 효율적.
=> 특정 SQL 쿼리를 나타내는 relation algebra 다양함.
practice
Q. 아래의 쿼리 표현할 relational algebra 생각해보기
SELECT s_name FROM student,takes,classes
WHERE t_sid = sid AND t_cid=cid
AND c_name = ‘6.830’
- A.
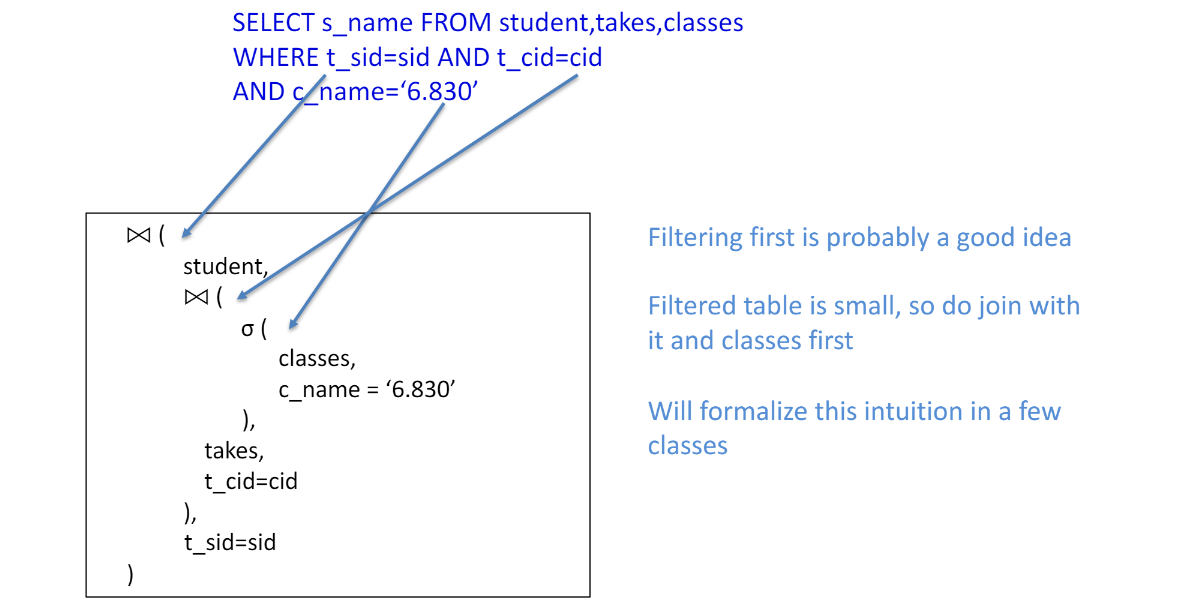
- select 후 join
지금까지의 내용
| IMS | CODASYL | Relational | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 중복(Redundancy)없이 다대다 관계 | X | O (선으로 연결하면 중복 X) | O (아예 set형태) |
| 선언적(Declarative)이고, navigational프로그램이 아닌가 | X | X | O (file저장된 형태 따라서 질의할 필요 X) |
Physical independence
: code 수정 없이 data의 representation 수정 가능
ex
SELECT a.name FROM animals AS a, cages AS c
WHERE a.cageno = c.noAND c.bldg = 32
- 물리적(physical) representation이 변경되어도 SQL의 변화 X
- CODASYL & IMS는 쿼리에 representation의존적인 연산 O
정리
| IMS | CODASYL | Relational | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 중복(Redundancy)없이 다대다 관계 |
X | O | O |
| 선언적(Declarative)이고, navigational프로그램이 아닌가 | X | X | O |
| Physical data independence (물리적 데이터 독립) |
X | X | O |
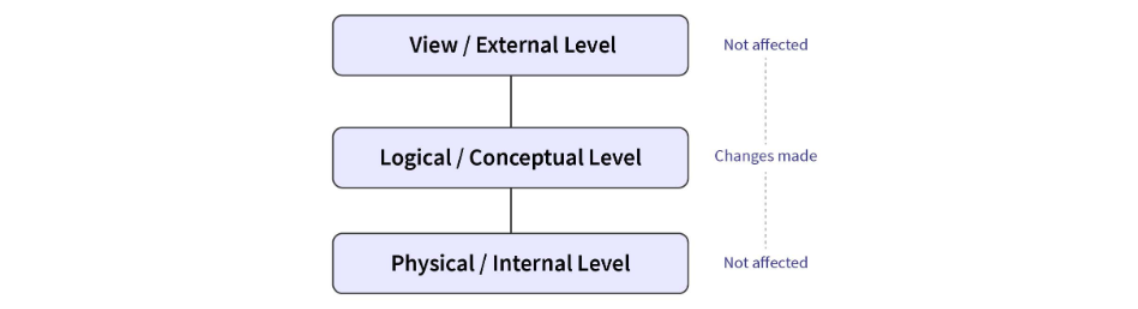
Logical data independence⭐
: 코드 변경 없이 schema 바꾸고 싶은 것.
-> column 혹은 table을 추가하는 경우 문제가 안됨.
View는 old 스키마를 new 스키마로 map 하는 것을 가능하게 한다.
따라서 old 프로그램 작동함. (존재하는 field 변경하는 경우에도)
View
: 다른 table에 대해 논리적 정의
= 새로 만들 table
예시
a view computing animals per cage
CREATE VIEW cage_countas
(SELECT cageno, count(*)
FROM animals JOIN cages ON cageno=no
GROUP by cageno)
view는 다른 쿼리의 table과 동일하게 사용될 수 있다
정리
| IMS | CODASYL | Relational | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 중복(Redundancy)없이 다대다 관계 |
X | O | O |
| 선언적(Declarative)이고, navigational프로그램이 아닌가 | X | X | O |
| Physical data independence (물리적 데이터 독립) |
X | X | O |
| Logical data independence | X | X | O |
핵심
- primary key
-
foreign key
- relational principles
- 단순한 representation
- ‘navigation’필요로 하지 않는 set-oriented 프로그램
- 물리적 데이터 모델 설명 요구 X
- relational data model
- 모든 data는 record(tuple)들의 table
- table은 unordered set들(중복X)
- db는 한개이상의 table
- 각 relation은 column/field의 type을 설명하는 schema 가지고 있음
- physical representation/layout 구체화(specify) X
-
relational algebra
- logical data independence
- 코드변경 없이 schema 변경하고싶을 때, column 혹은 table 추가하는건 문제없음
- view는 구 schema를 신 schema로 map해주어 old program들이 동작할 수 있게 함.
- views example
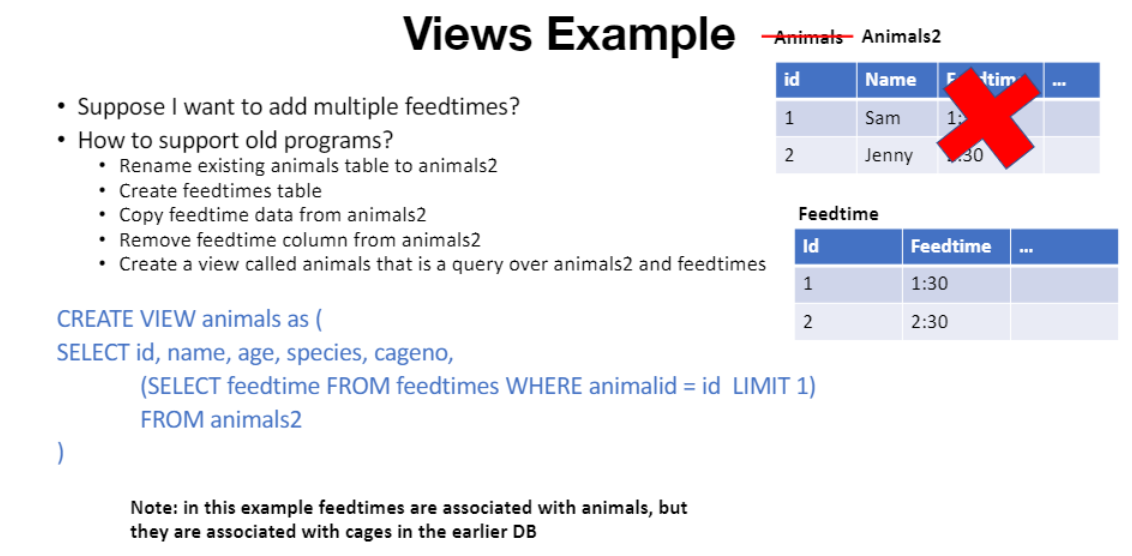 Q. 과거 table 지우고 새 table 생기면, 이전 schema 어떻게?
Q. 과거 table 지우고 새 table 생기면, 이전 schema 어떻게?
-> A. view 만들자
출처 : 2023-2 ITE2038 수업