Amortized Analysis_Dynamic Table (4/4)
ITE2039 Algorithms and problem solving
Amortized Analysis
이전까지 operation의 asymptotic boundary 구했음. (e.g. sort 비교횟수-> boundary)
이 chapter에서는, push-pop 할때 push와 pop 수행시간 각각 구해서 합하는게 아닌, push, pop 합해서 n번 발생했을 때 전체 cost 구하는 것.
= 독립적으로 시간복잡도 구하는 것이 아닌, 여러 operation의 시퀀스 한꺼번에 시간복잡도 분석.
(최악의 경우를 과하게 잡지 않도록)
특정 일을 할 때 100번 진행하는 경우 99번 1분이 걸리고, 1번정도 10분이 걸린다. 이때 최악의 경우 10분으로 잡고 이 일을 반복하는 횟수를 곱하게 되면 너무 과하게 upper bound를 잡는다는 것에서 시작.
각 시퀀스의 upper bound를 구하고 이를 진행 횟수만큼 곱하는 것이 아닌 한번 진행할 때에 대한 평균적 시간을 구해서 upper bound를 구하자.
n회 진행 시 총 걸리는 시간 T(n)을 구할 수 있다면 T(n)/n이 한번 진행시 걸리는 시간이고, 이것이 한번 진행했을 때 최악의 시간(위 예시에서 10분) 보다 짧다면 평가절하를 줄인것.
amortized 예시
참고
Contents
➖ Aggregation analysis
➖ Accounting method
➖ Potential method
☑️ Dynamic Table
Dynamic Table
Table 할당(allocation)문제
우리는 얼마나 많은 object가 table에 저장될지 항상 아는건 아니다.
Table에 object를 추가하는 경우 대부분의 연산은 O(1)의 비용이 들지만, 테이블이 가득 찬경우 새로운 테이블 생성하고 기존 table에 있던 object들을 복사해야하기 때문에 O(n)비용이 드는 연산이 발생하기도 한다.
Aggregate analysis
INSERT- 가득찬 table에 insert 하려는 경우, 기존 table보다 더 많은 slot을 가지는 새로운 table로 allocate함으로써 table expand
T.table: table을 나타내는 storage block을 가리키는 pointerT.num: table의 item #T.size: table의 총 slot #
TABLE-INSERT(T, x)
if T.size == 0
allocate T.table with 1 slot
T.size = 1
if T.num == T.size
allocate new-table with 2 * T.size slots insert all items in T.table into new-table // elementary insertion
free T.table
T.table = new-table
T.size= 2 * T.size
insert x into T.table // elementary insertion
T.num= T.num+1
- 새로운 item을 위한 공간이 있는 경우,
cost $c_i=1$ - current table이 가득차서 expansion 발생 시,
$c_i=i$- 새로운 item insert하는 데 1, 확장을 위한 이동에 $i-1$
- initially empty table에 n회
TABLE-INSERToperation 하는 경우 시퀀스 분석
$c_i=\Big{ \begin{matrix}i ~~~~if~ i-1~ is~ an~exact~power~of~ 2(테이블 확장)\1 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ otherwise (테이블 안늘려도 되는 경우)\end{matrix}$power of 2인 이유:
table 늘릴 때 2승 크기로 늘려서 TABLE-INSERToperation의 total cost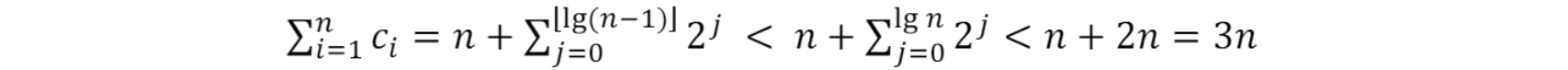
#69-74 skip
Accounting method
출처 : 2023-2 ITE2039 수업