-----DRAFT-----ITE4052_CV > 4_3D Vision
3D Vision
목차
- 2D -> 3D 변환 시 문제점, 해결방안
- Stereo
Inverse Perspective Transformation
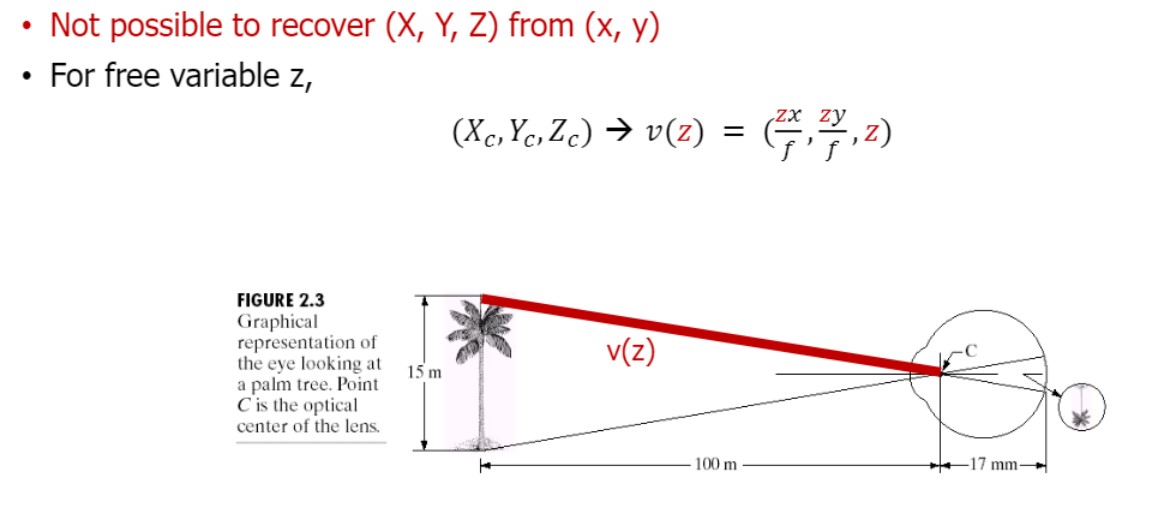
(single view image로)
2D -> 3D 변환 시 문제점:
이미지의 Z값을 위 사진의 빨간 선 중에서 확정 지을 수 없다는 ambiguity(모호성) 때문에 불가하다.
(완벽히 3D recover 할 수 없다)
따라서 3D를 reconstruct하려면 multiple view가 필요함 (적어도 2개)
Stereo
다른 viewpoint의 두 이미지가 있을 때, 어떻게 각 point의 depth(z) 계산하지?
-> 키 아이디어는, 두 이미지의 disparity (how much each pixel moves)를 찾는 것.
이번 장에서는 두대의 카메라가 이상적으로 있는 경우만 봄.
즉,
camera intrinsic parameter인 K동일
$K_{1} = K_{2} = K$
no Rotation
$R = I$
translation은 x축으로만 있는 경우
$t = (t_{x},0,0)$
그리고 두 카메라 간의 거리를 baseline (= $t_{x}$)라고 함
추가적으로 $t_{x}$는 stereo의 base line이라고도 함
Epipolar Geometry

완벽히 horizontal한 경우 (z축으로만 translation있는 상황)
(x1,y1)과 (x2,y1)이 대응한다.
이 경우 y값 차이 없이 x값만 차이있음
그리고 $y=y_{1}$인 horizontal line이 epipolar line
Epipolar Line – X X X
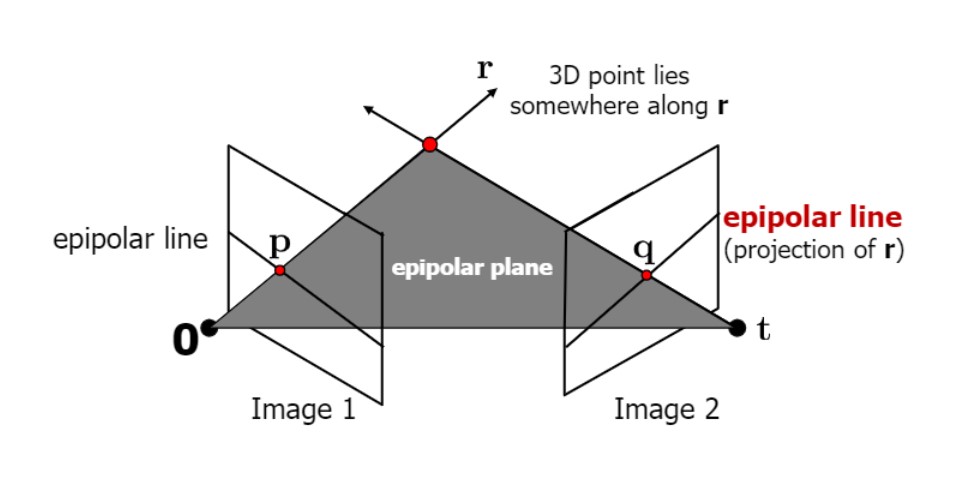
Image1의 한 점은 Image2의 epipolar line 하나에 항상 대응
이번학기에는 epipolar line이 horizontal line인 이상적인 case만 다룸
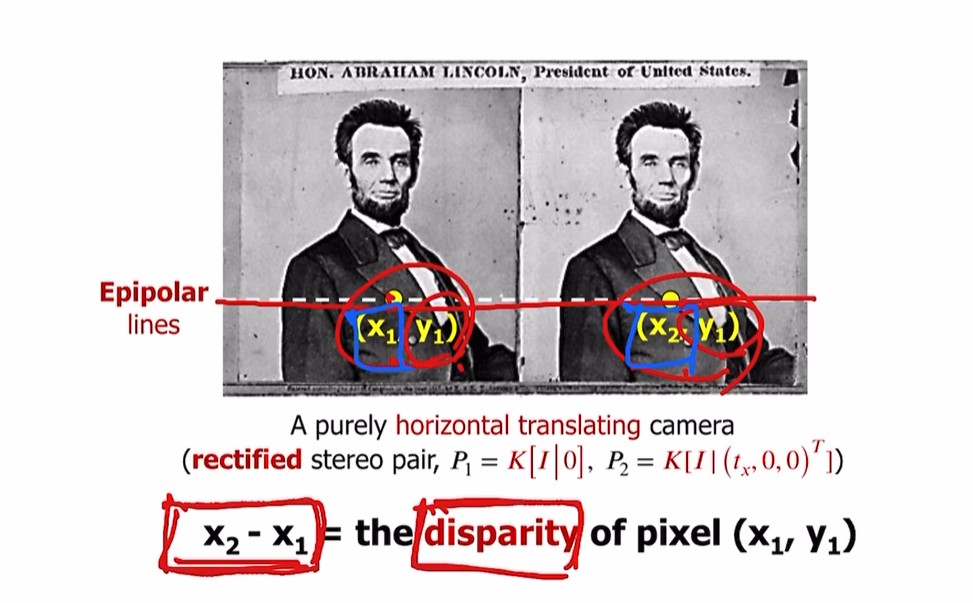
선 위의 이미지 1의 한 점은,
이미지 2의 선 위의 한 점에 대응할 것이다.
-> 결국 두 점이 대응한다는 것이고,
두 뷰의 차이가 존재할 것이다. 그리고 그 차이를 disparity라고 함.
$\therefore$위의 링컨 이미지로 예를 들면,
$x_{2} - x_{1} = $ the disparity of pixel $(x_{1}, y_{1}) $
disparity = 같은 object의 두 view에서 pixel level difference
Depth from disparity
disparity ** stereo matching에서 가장 중요한 개념
$\because$ disparity 통해 depth 예측할 수 있음
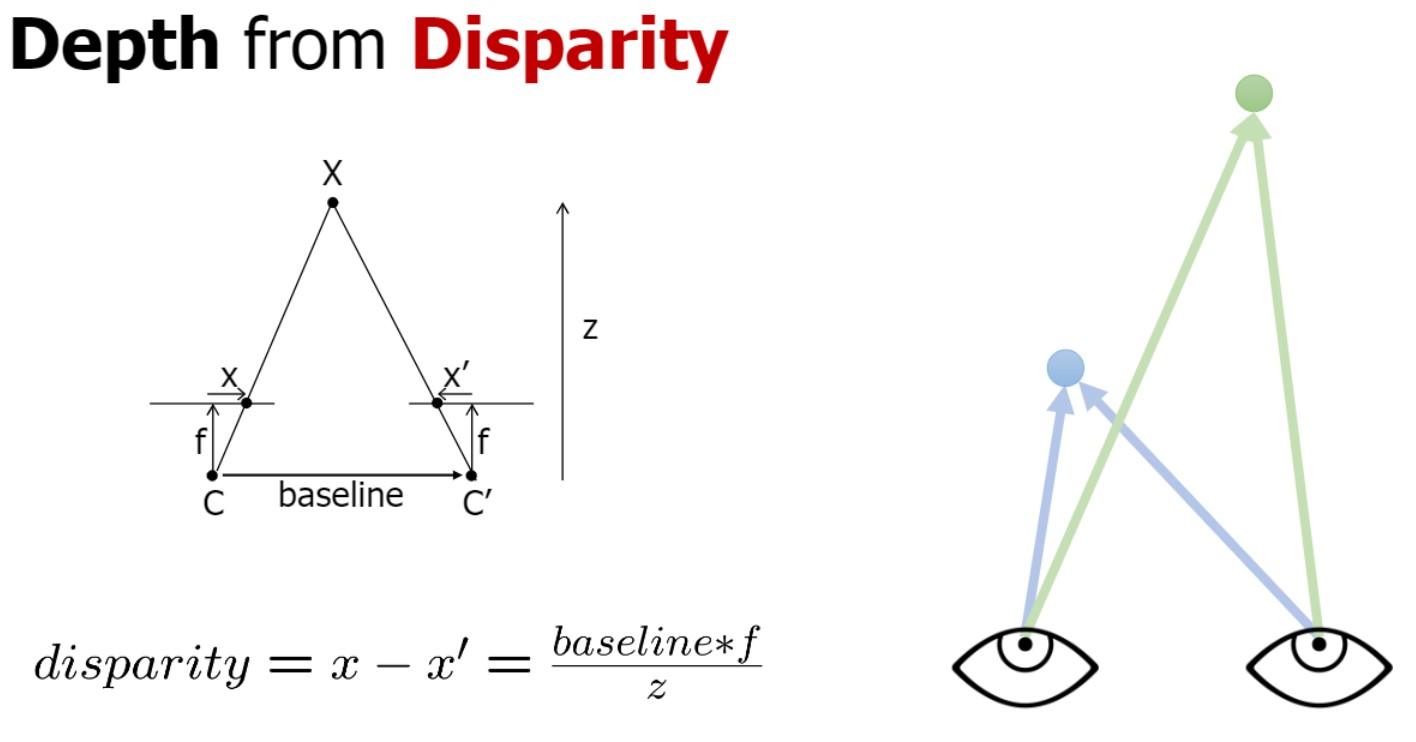
픽셀레벨의 차이인 disparity / f = baseline($t_{x}$) / z
depth와 disparity는 항상 반비례 관계
small disparity → (z큼) = far location
large disparity → (z작음) = close location
Disparity = Inverse Depth
-
large disparity → close region
-
small disparity → far region
stero matching의 첫번째 중요한것이 disparity
=> 결국 “3D reconstruct problem = 적절한 Disparity값 찾는 문제”로 볼 수 있다
3D vision(혹은 stereo matching)에서 중요한 키워드 두가지
- 적절한 correspondence 찾기
- compute disparity
+ criterion(기준) of finding correspondence is match cost
Stereo Matching

follow line, get one point, 우측에서 점 찾기
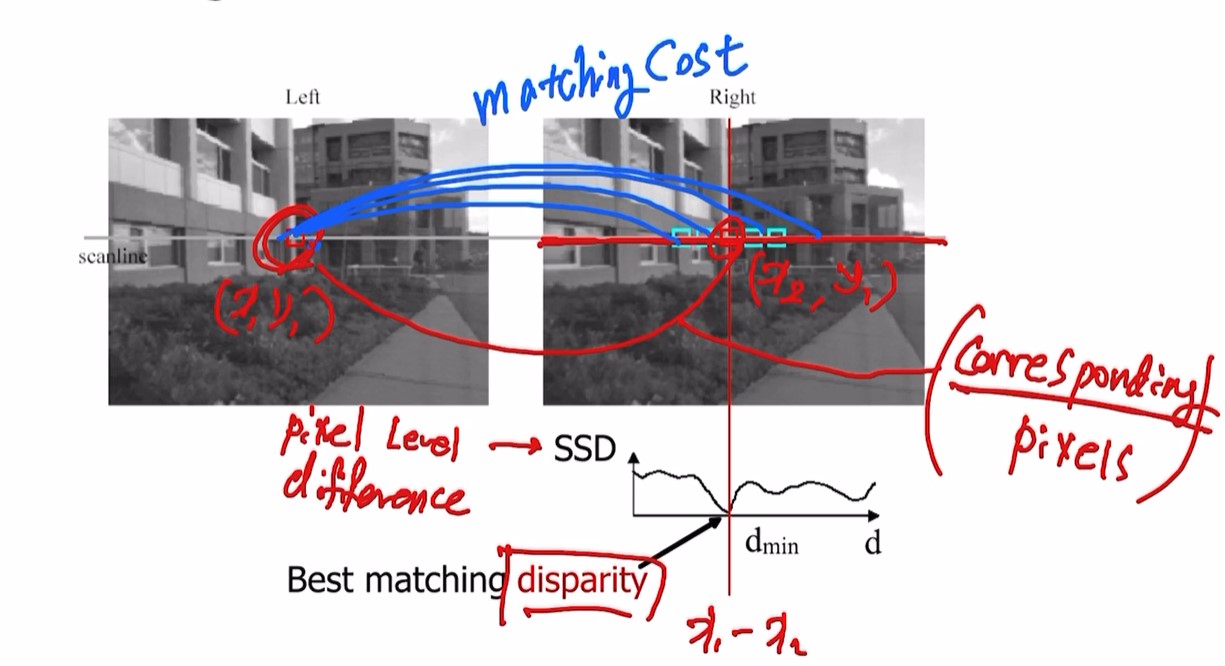
stereo matching 과정 ❗
-
좌측 이미지의 한 점 선택
-
선택한 점과 우측 이미지의 epipolar line에 대응하는 모든 점간의 similarity 비교. = matching cost
(SSD = pixel level difference)
-
이후 least difference value 주는 픽셀 찾기
이 둘이 corresponding pixels.
두 점의 x좌표를 안다면 바로 x1-x2인 disparity 구할 수 있다. -
모든 픽셀의 disparity value를 찾으면 matrix인 disparity map이 만들어짐.
우측 이미지가 disparity map visualization 결과
Stereo Matching results
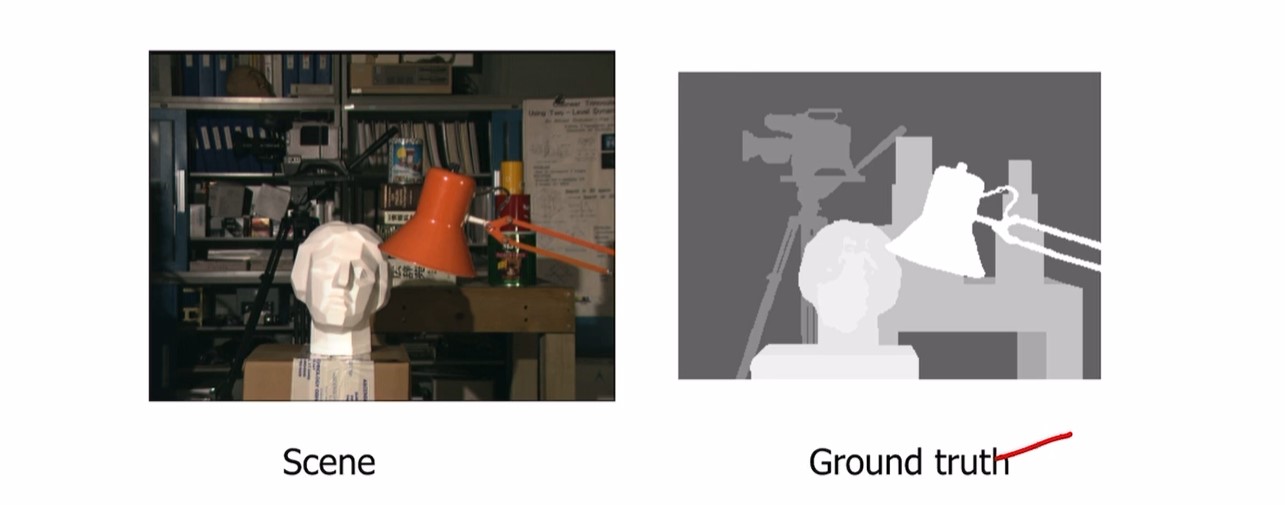
위 이미지에서 본 형태가 우리가 원하는 이상적인 형태이지만
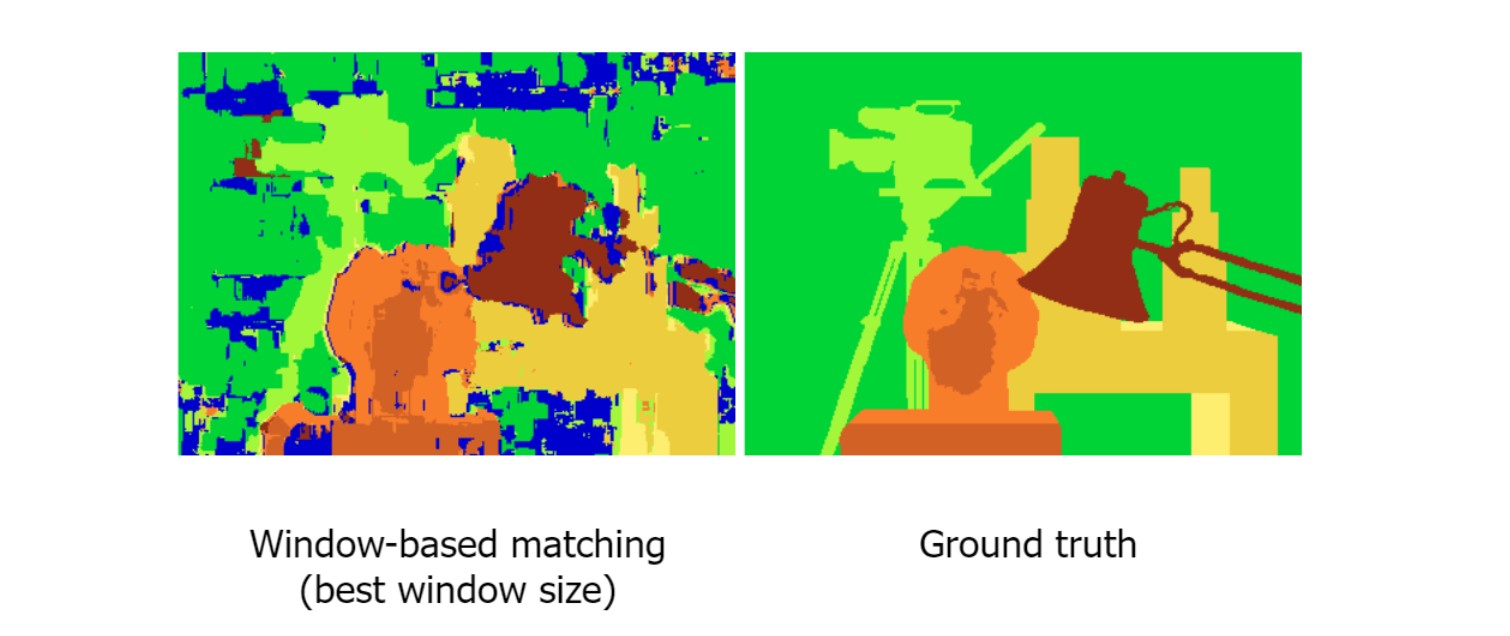 좌측이미지처럼 noisy 할것임.
좌측이미지처럼 noisy 할것임.
다양한 이유가 있지만,
similarity measure가 완벽하지 않음
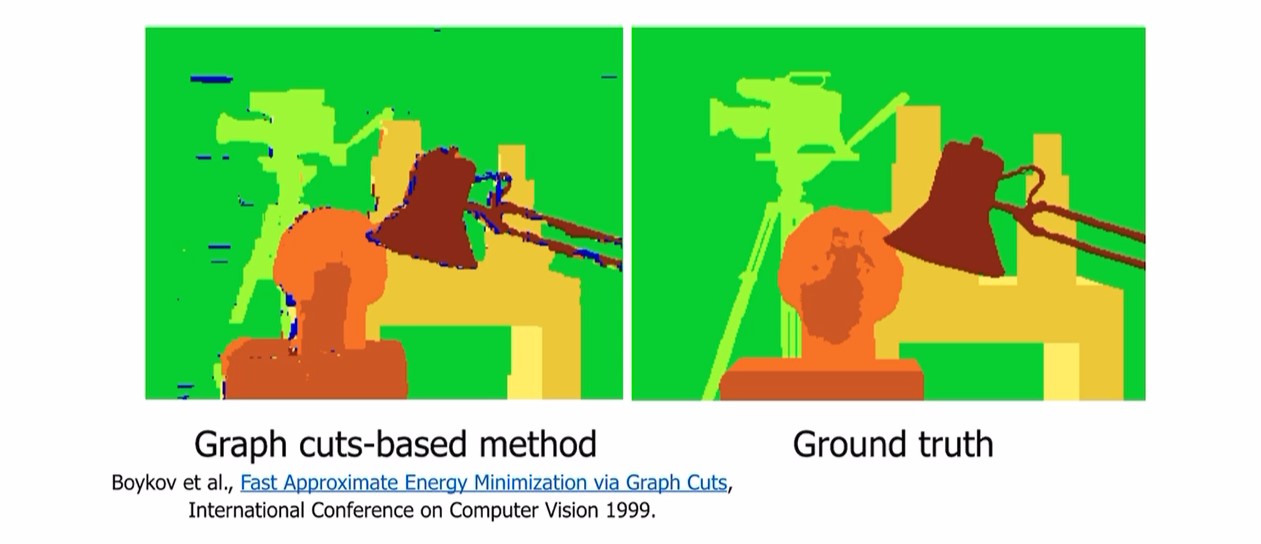 smoothing 알고리즘과 같은 다양한 cost processing 알고리즘을 적용할 수 있다
smoothing 알고리즘과 같은 다양한 cost processing 알고리즘을 적용할 수 있다
smoothing의 한 예시로 graph cut
matching cost에서 적용할수도 있음
Q. 어떻게 matching cost를 stereo matching에서 적용?
A. Stereo matching을 Energy optimization problem으로 생각(= 딥러닝의 loss minimization과 같이 energy minization)
disparity map으로부터 얻고싶은 criterion은?
- Matching quality
만약 두 픽셀(각 뷰에서 하나씩 총 2개)이 같은 object로부터 왔다면 good match(높은 pixel level similarity)를 가져야 한다.
- Smoothness
Disparity map에 더 많은 constrain 더해야 한다
한 object의 두 점은 유사한 depth값을 가져야 한다
Energy minimizaton
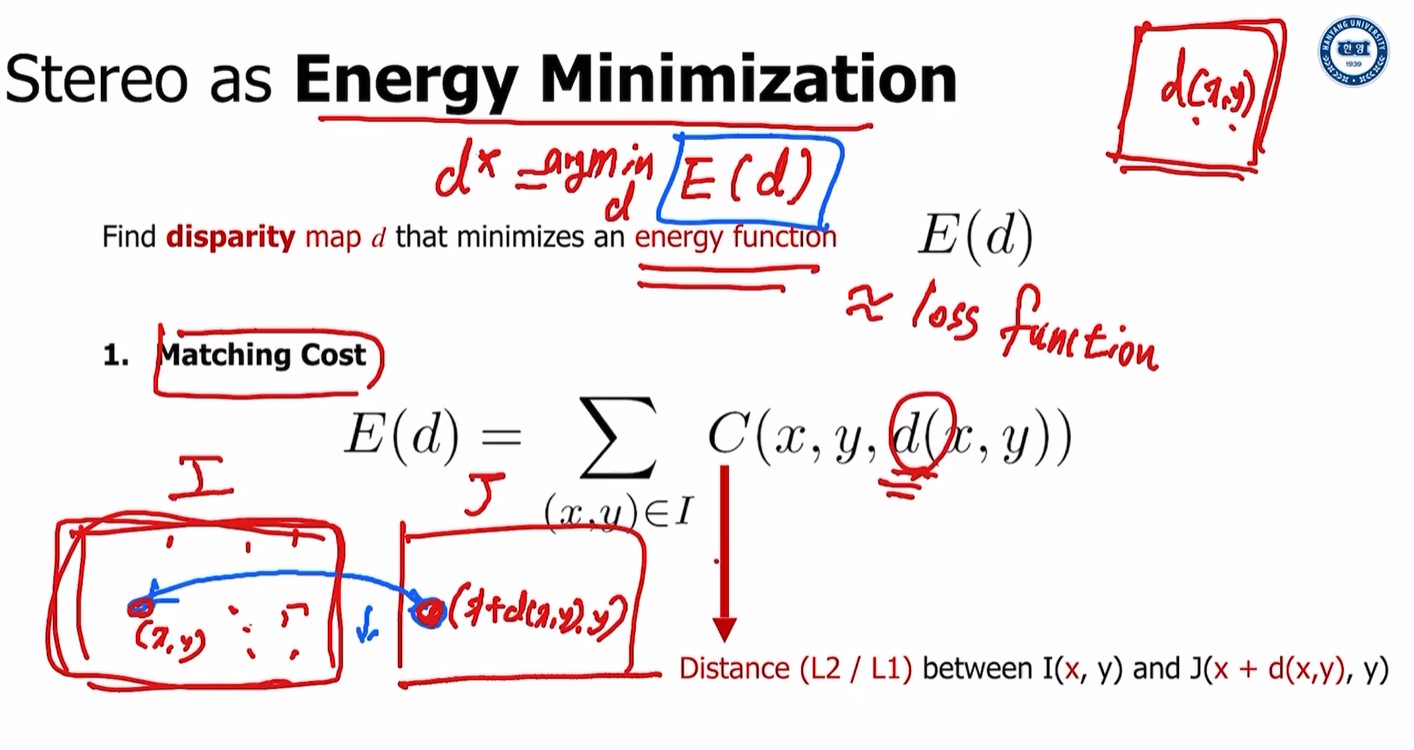
d(x,y)라는 disparity map 혹은 x,y location의 function of disparity value 있을 때
우리는 minimum energy value 주는 완벽한 disparity map을 얻고 싶다.
disparity value가 d(x,y)인 두 뷰 I, J 있을 때,
I의 (x,y)는 J의 (x+d(x,y),y)와 대응.
그러면, 두 픽셀의 pixel level distance가 가능한 한 최소여야 함
(모든 픽셀에 대해)
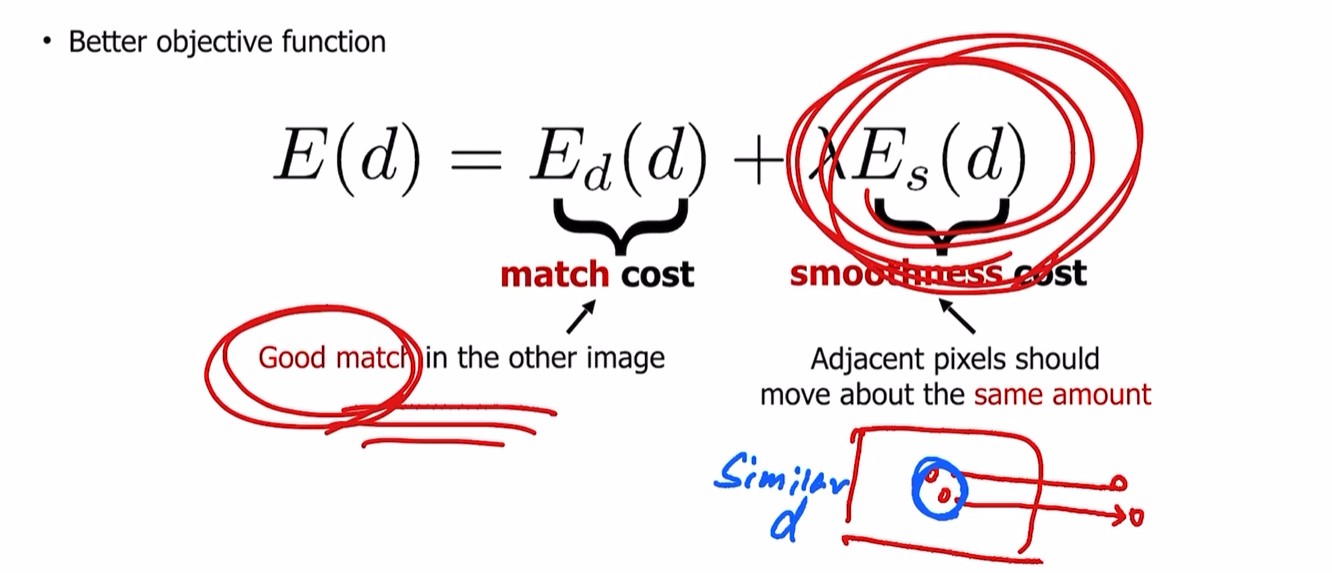
다시말해서 우리는 disparity map이 완벽하길 바란다. 따라서 (x,y)와 (x+d,y)의 pixel level distance가 최소화 되기를 원함.(모든 픽셀에서)
따라서 noisy 한 결과가 나오고, 그렇기 때문에 smoothness cost를 더해야 함.
smoothness cost는 두 픽셀이 같은 object로부터 나왔다면 같은양만큼 움직여야 한다. disparity between near pixel should be similar(= near pixel -> similar d)
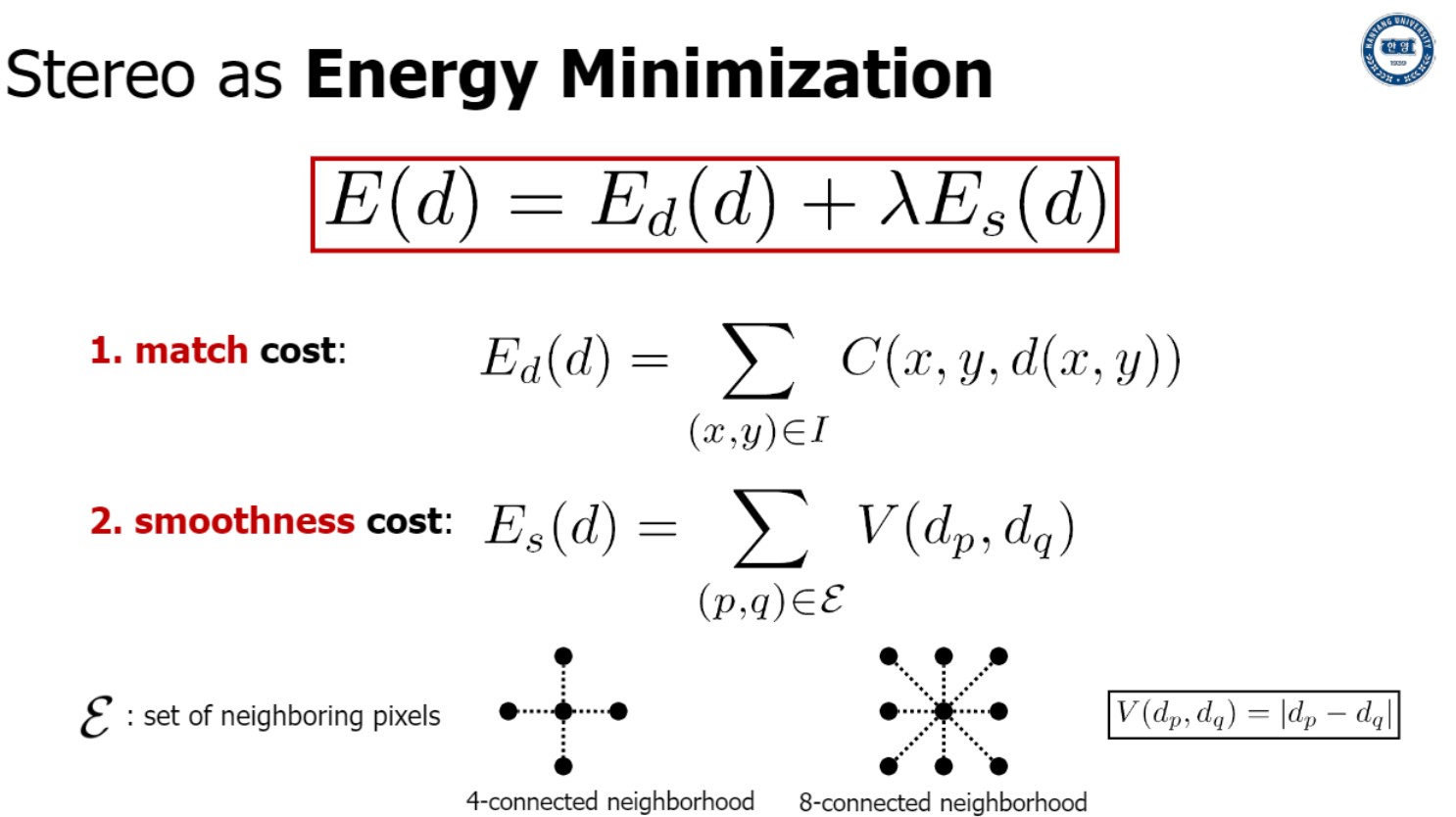
전형적인 stereo matching은 두 objective(match cost, smoothness cost)의 합으로 정의될 수 있다.
첫번째 match cost는 두 view 사이의 cost. 가능한 higher similarity small distance
두번째 smoothness cost는 한 뷰의 (근처 두 점의)disparity가 유사 해야한다 (계산시 보통 L1 distance사용)
“near pixel” 어떻게 정의하는가?
near 4 pixel, near 8 pixel
❗❗ Stereo matching의 중요한 두개의 objective가 무엇인가? 라고 하면
1 match cost와 2 smoothness cost 말하고 설명할 수 있어야 함
Multiple-view stereo
: object의 3D shape 알기 위해 3개 이상의 multiple 이미지 사용
우선 모든 카메라가 calibrated 되었다고 가정
즉, 모든 뷰의 K값과 모든 카메라 파라미터($[R|t]$ in P) 안다고 가정
calibrated 안 된 경우는 좀 이따.
Multiple-view stereo의 basic idea
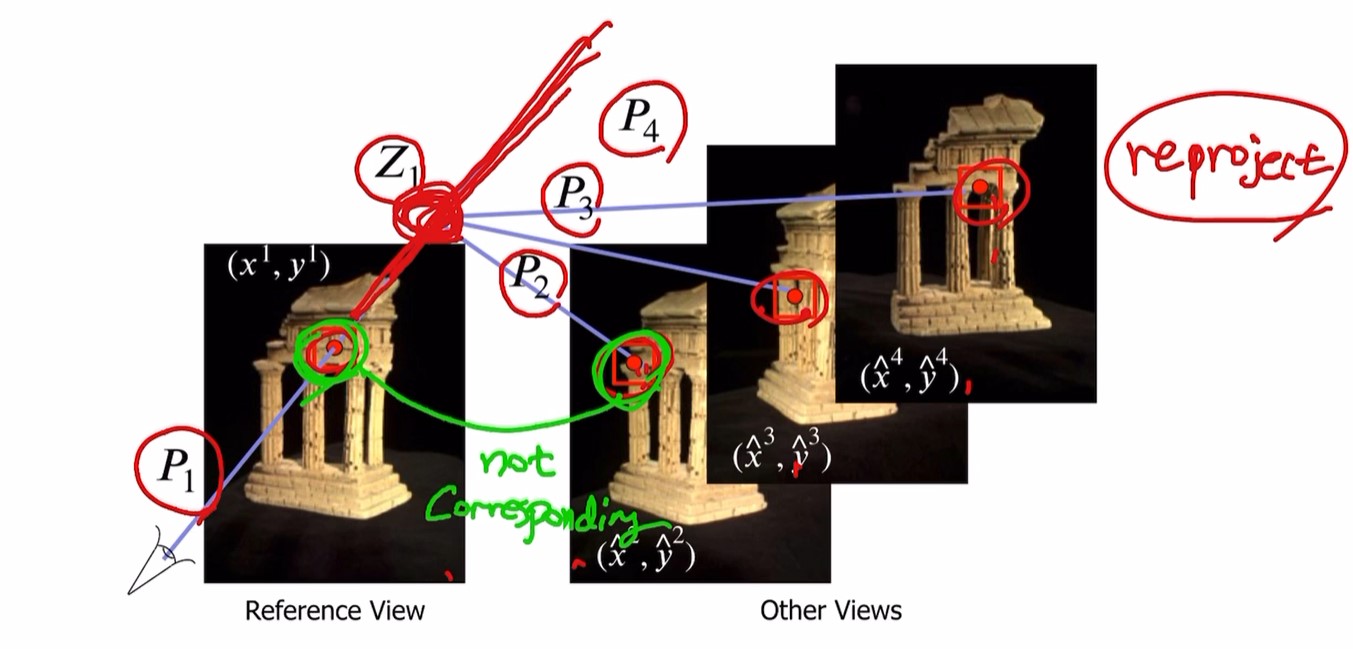
여러 view가 있을 때 (reference 이미지의) 한 점에서 시작.
카메라 matrix $P_{1}$을 알기 때문에 3D object가 있을 가능성이 있는 ambiguas line을 구할 수 있음
선 위의 한 점($Z_{1}$)에서 시작.
다른 모든 카메라들의 parameter($P_{2}, P_{3} …$)를 알기 때문에
가정한 object의 3D location으로부터 각 뷰로 reproject 할 수 있음.
하지만 각 점이 corresponding 하지 않다는 것을 알 수 있음.
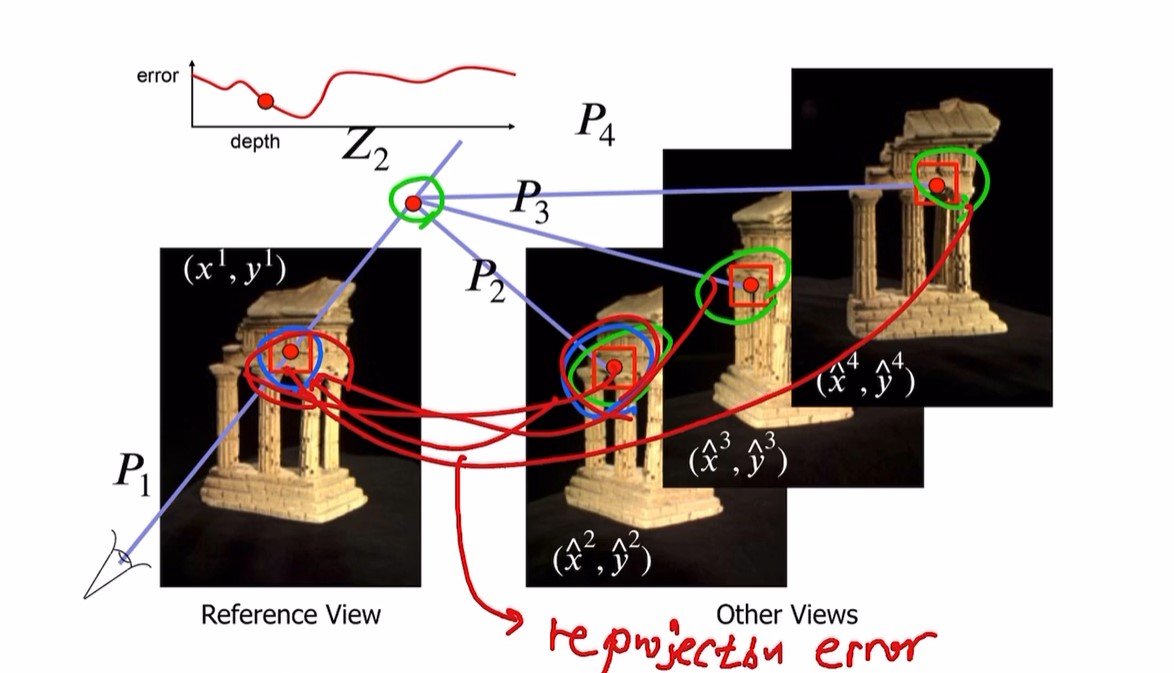
다른 점에서 reprojection.
이후 각 뷰의 점이 corresponding한지 reprojection error로 확인.
이 과정을 반복 후
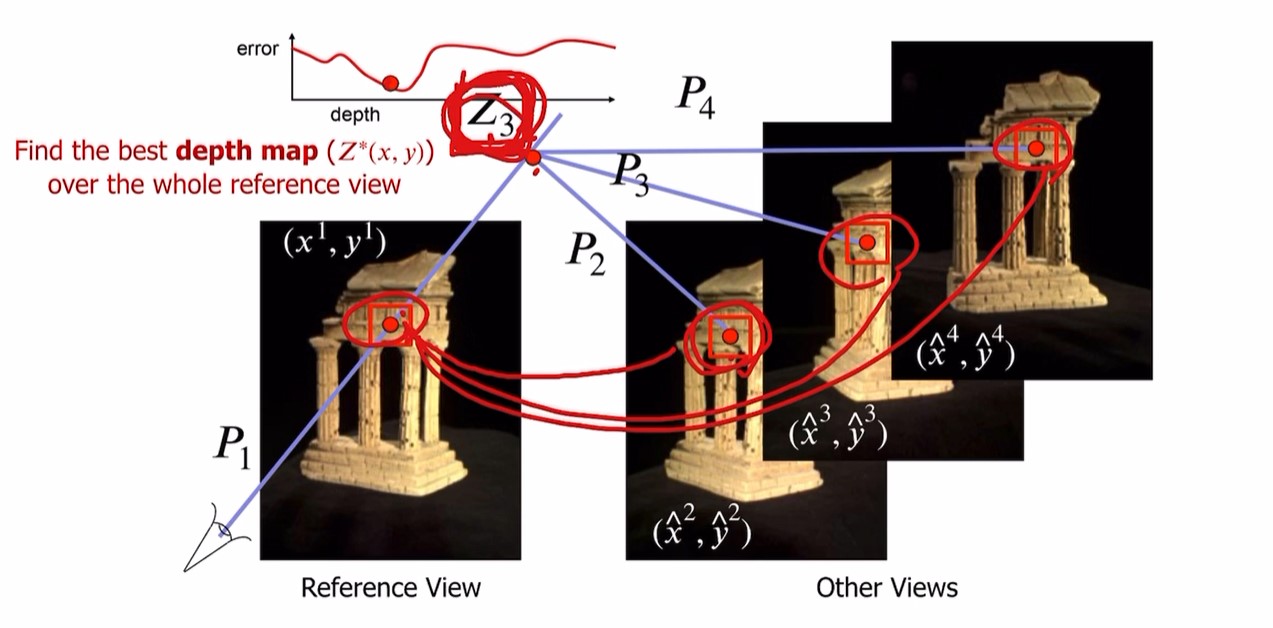
이 reprojection result가 original view에 완벽히 corresponds => 적절한 Z 값
정리하자면,
multiple-view stereo의 기본적인 아이디어는,
선 위의 점 Z를 바꿔가면서
각 x,y로부터 best depth value를 찾는 것.
가능한 Z 값들의 reprojection error를 비교하면서 우리가 원하는 값인 완벽한 Z 값 찾음.
그리고 이 과정을 모든 픽셀에 대해 진행하여 depth map 구함.
결국 우리가 원하는건 depth map인 Z(x,y)
1:10:00 이미지?
Plane-sweep stereo
depth의 다양한 assumption을 통해 적절한 3D 위치 찾는것.
multiple view에서 각 픽셀마다 완벽한 correspondence를 주는 z값이 다르다
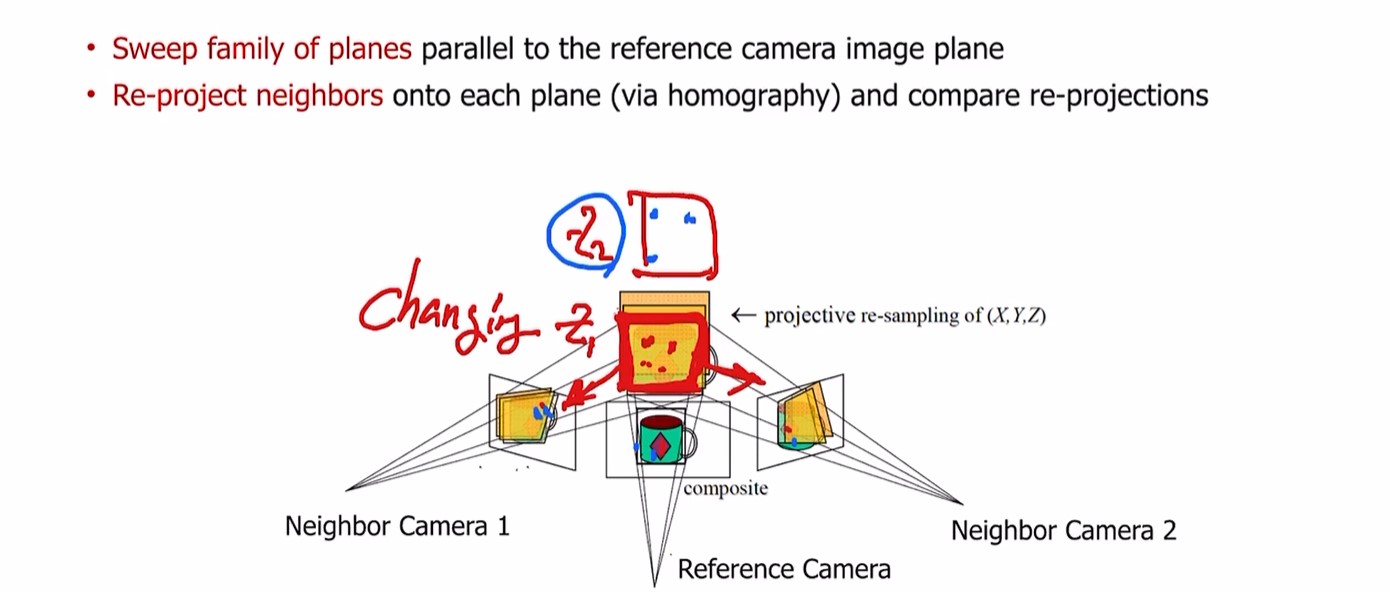 다양한 z값으로 plane 변경
다양한 z값으로 plane 변경
선택한 plane을 각 뷰에 reprojection.
각 픽셀마다 perfect correspondence 찾을 수 있는 z값이 다르다.
plane 움직이면서 reprojection error 계산해서 각 픽셀마다 error 최소화 된 z 값 찾기.
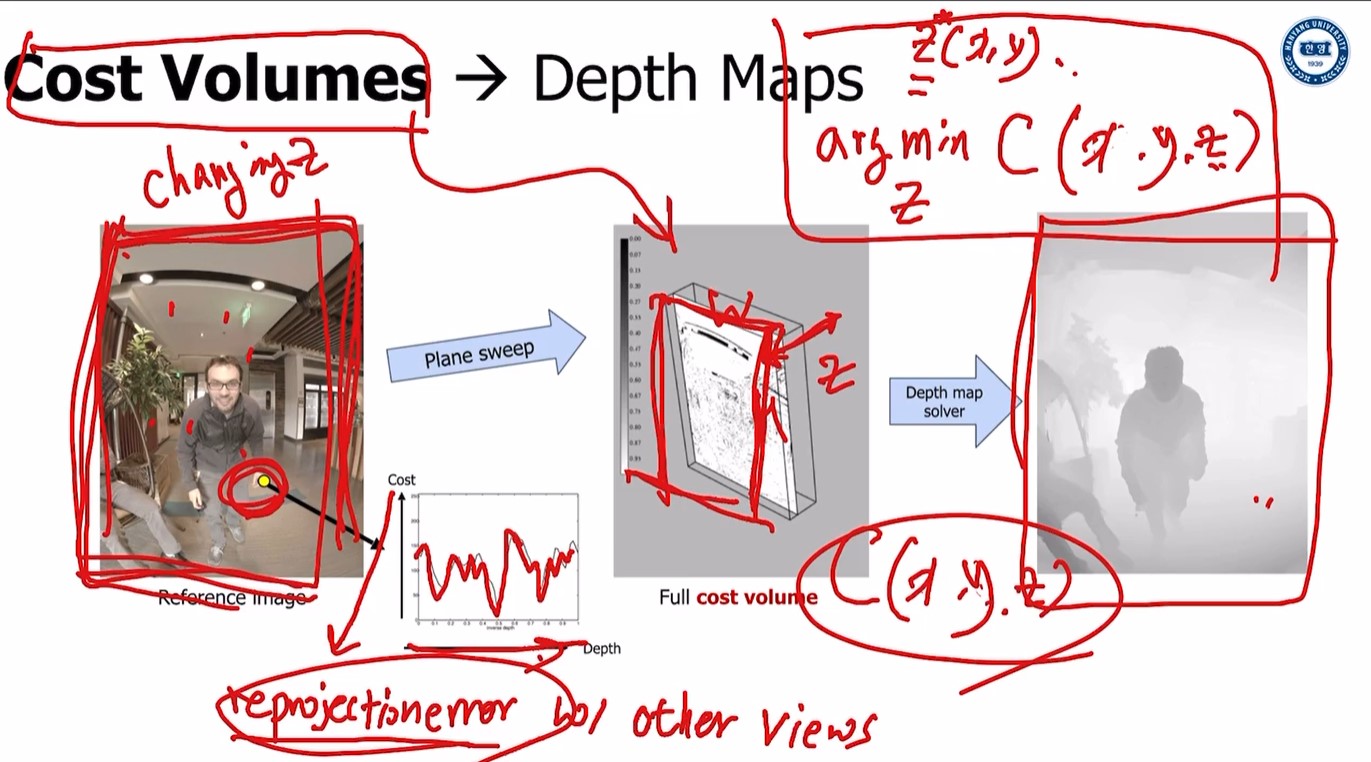
먼저,
z 값을 변화시키면서 plane 움직인다.
다른 view로 reproject 하면 각 픽셀마다 reprojection error 찾을 수 있다.
(이미지의 그래프가 depth인 z값의 변화에 따른 cost변화)
위 연산을 하면 각 z값마다 W x H matrix가 나오고, z값들을 stack 하면 이미지 중앙의 W x H x Z 크기의 cost volume을 얻을 수 있다.
그리고 arg min z를 하면
각 point의 depth map는 가장 낮은 cost volume(= least reprojection error)을 가진 best z값을 통해 최종적인 depth map을 얻게 된다.
Structure-from-Motion (SfM)
(이것이 더 일반적인 경우)
지금까진 카메라 캘리브레이션 파라미터를 다 안다고 가정했었음.
몇천개의 카메라가 있다면 hard to calibrate all!
따라서 일반적인 경우 모든 카메라가 calibrated 되었다고 가정하기 어려움.
따라서 이러한 structure from motion의 경우, 다른 카메라 파라미터 모르는 경우.
그리고 structure from motion문제를 해결하면서, 우리는 3D structure인 X와 카메라 matrix인 $K[R|t]$ 둘 다 찾을 수 있다.(이것이 SfM의 output)
Large-Scale Structure-from-Motion
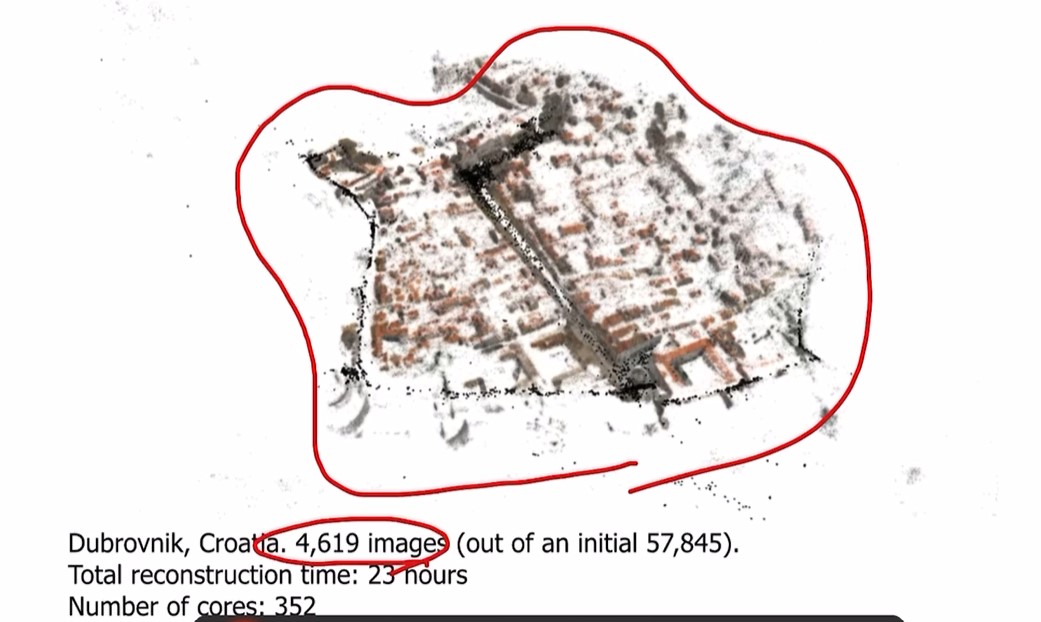
SfM알고리즘으로, 몇천개의 이미지를 통해 한 city의 3D structure를 구할 수 있다.

video에도 적용 가능. SLAM(simultaneous localization & mapping)이라고 함
mapping은 3D structure를 찾는 것(finding X value)
localization은 카메라가 어디에 있는지 찾는 것(finding P value)
SLAM과 SfM의 차이:
SLAM은 한 카메라로 움직이면서.(same, moving camera)
SfM은 모든 카메라는 각각의 다른 카메라, 각 카메라의 intrinsic parameter도 찾아야 함.
Input to Structure from Motion —> 아직 부족
이전에 말했듯이 SfM은 카메라 matrix value를 모른다.
따라서 이 문제를 해결하기 위해선 더 많은 정보가 필요하다.
=> “Feature Correspondence”(stereo matching problem에서 봤음)
SfM전에, 성능이 좋은 Correspondence search 알고리즘으로 여러 뷰의 완벽한 correspondence를 안다고 가정.
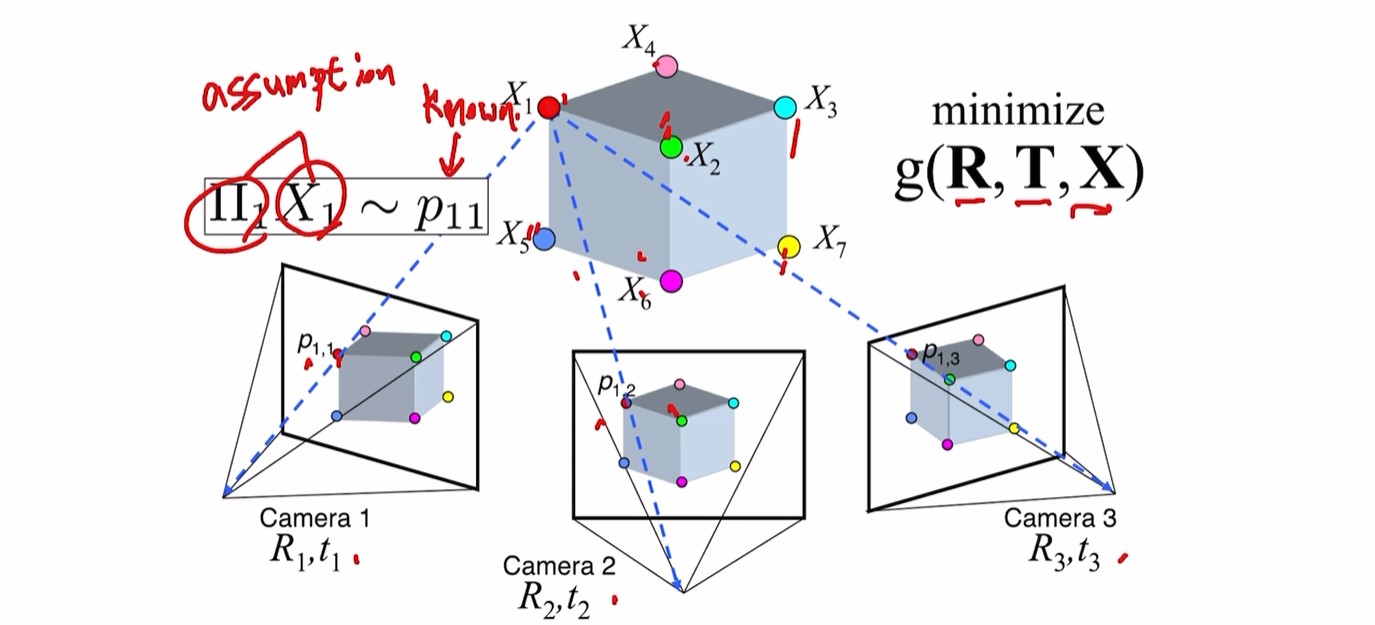
이후, 완벽한 correspondence를 알고있기 때문에, 각 Corresponding point로부터 3D 구조 assume.
이후 각 카메라에 대한 rotation, translation도 예측
?
g(R,T,X) 예측할 때마다 correspondence를 찾으며 point가 일치하는지 확인
?
g(X,R,T) 즉 location과 카메라 parameter 예측하고 있음
현재 corresponding은 알고있다고 가정하고 있으니,
reprojected 이미지가 corresponding관계인 ground truth와 일치하는지 비교
알고있는 위치와 reprojected 위치의 차이 최소화
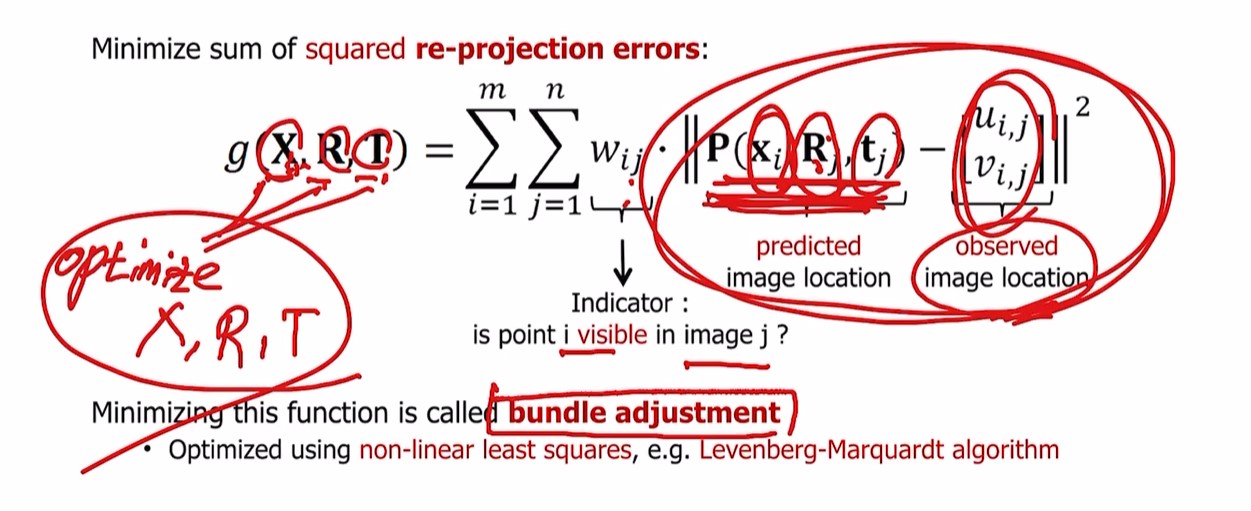
주어진 $x_{i}$와 예측한 $R_{j}, t{j}$로 j이미지의 reproject한 region과 ground truth인 $u_{i,j}, v_{i,j}$가 일치해야 한다.
bundle adjustment는 re-projection error에 기반해서 위 수식의 과정을 optimize 하는 것
다른 optimization method들도 존재하지만,
절댓값 기호 안쪽 부분의 reprojection error 부분을 이해하는것이 중요.
NeRF
출처 : 2023-1 ITE4052 수업