Elementary Graph Algorithms part1:Graphs
ITE2039 Algorithms and problem solving
Contents
- Graphs(part1)
- Graph basics
- Graph representation
- Adjacency-list representation
- Adjacency-matrix representation
- Searching a graph (part2)
- Breadth-first search
- Depth-first search
- Applications of depth-first search(part3)
- Topological sort
Elementary Graph Algorithms 1
Graph basics
- Graph G는 V와 E의 쌍. (V,E)
(V: vertex, E: edge)- vertex는 아래 그림에서 원형인 node
- edge는 아래 그림에서 선인 link
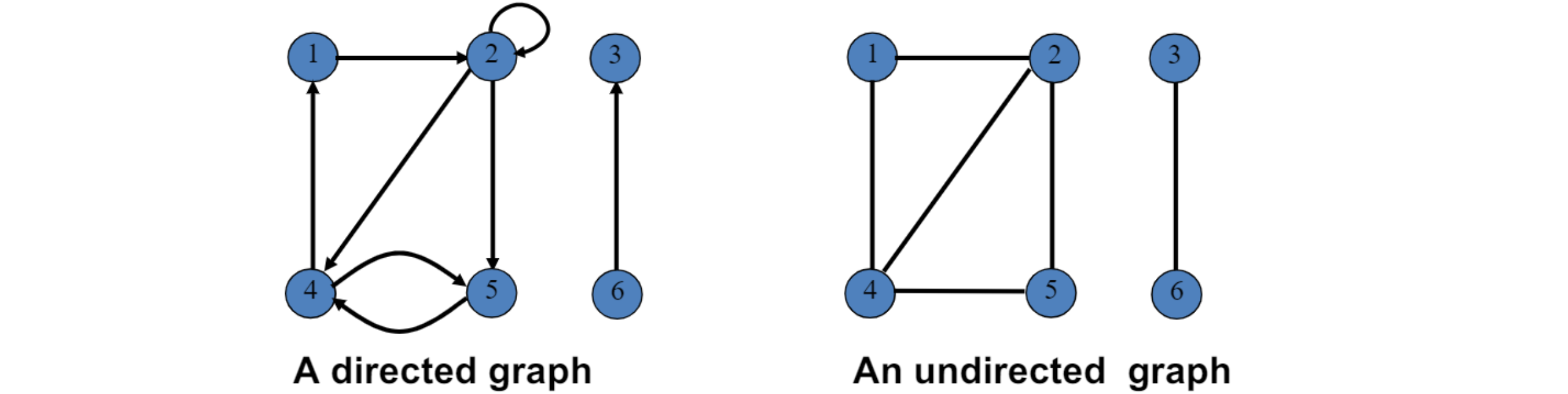
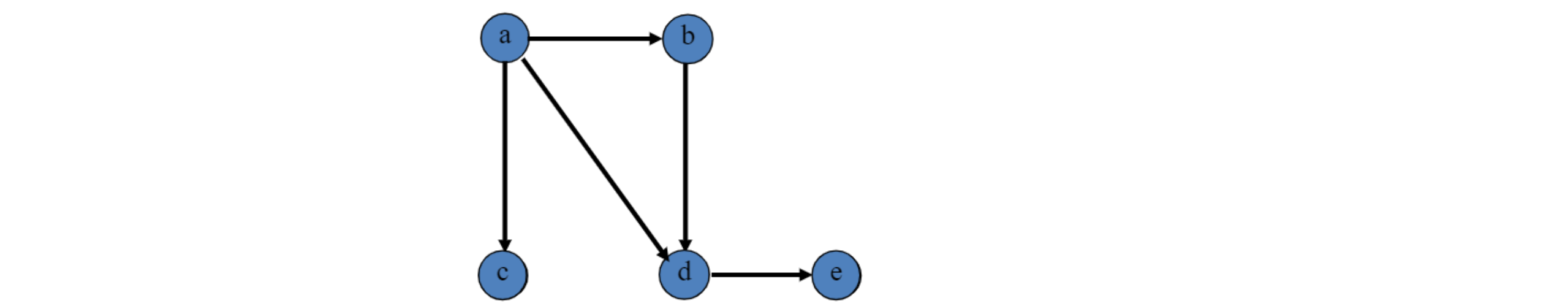
- Directed graph (= digraph)
- 아래 파란색 edge는 incident from vertex 2,
incident to vertex 4- incident는 edge와 vertex 사이의 관계를 나타냄
- 빨간색 edge는 self-loop
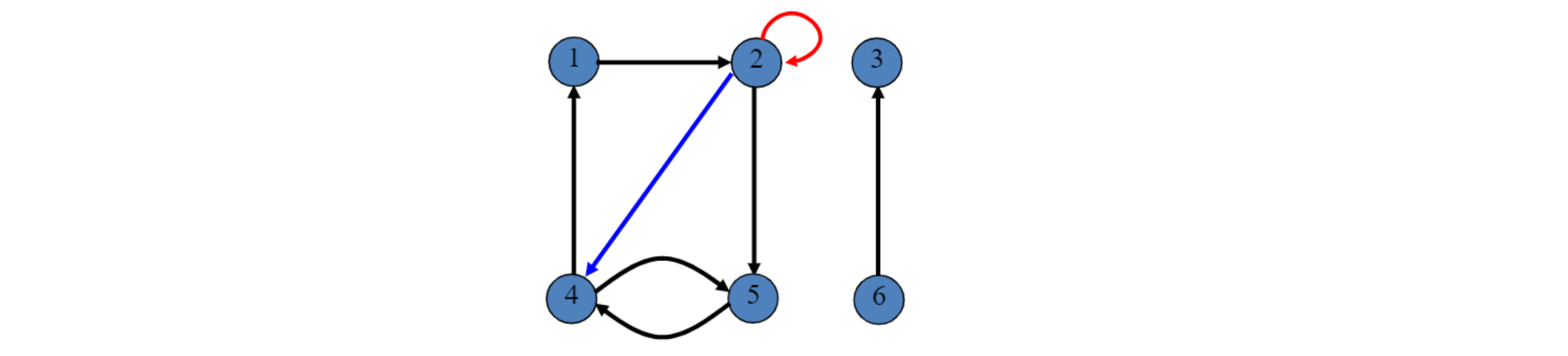
- 아래 파란색 edge는 incident from vertex 2,
- Undirected graph
- edge가 direction가지고 있지 않음
- self loop 없음
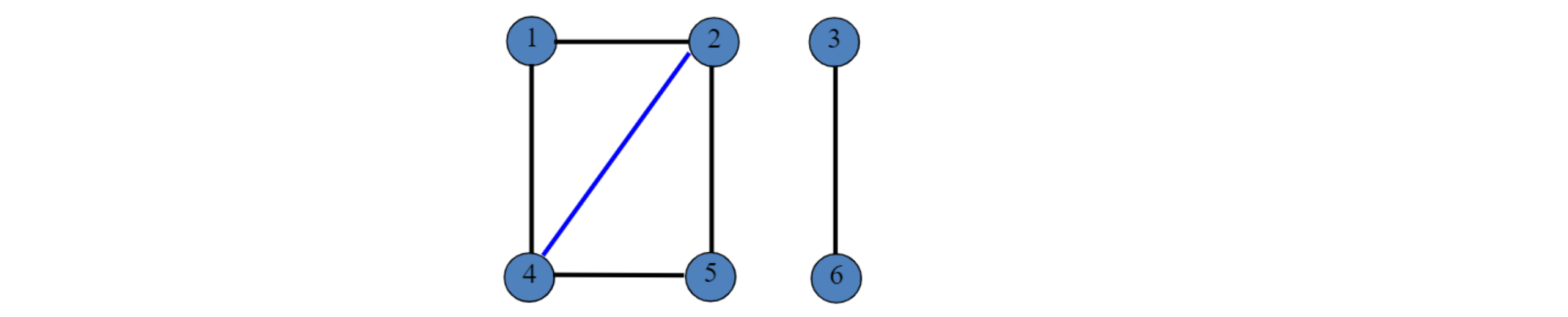
- Adgacency (= 노드사이의 관계)
- 만약 (u,v)가 edge라면, vertex v is adjacent to vertex u
- undirected graph에서는 adjacency관계는 대칭(symmetric)
- u is adjacent to v이면, v is adjacent to u
- directed graph에서는, 대칭 관계가 아님! (❗주의)
- 아래 그림에서, vertex 2 is adjacent to 1
- 하지만 vertex 1 is not adjacent to 2

- Degree
- vertex 2의 out-degree는 3
- vertex 2의 in-degree는 2
- degree = out-degree + in-degree

- Path
- 연속적인(consecutive) edge의 sequence
- 여기서 주의할 점은 edge의 ‘순서’라는 것. 집합 아님!
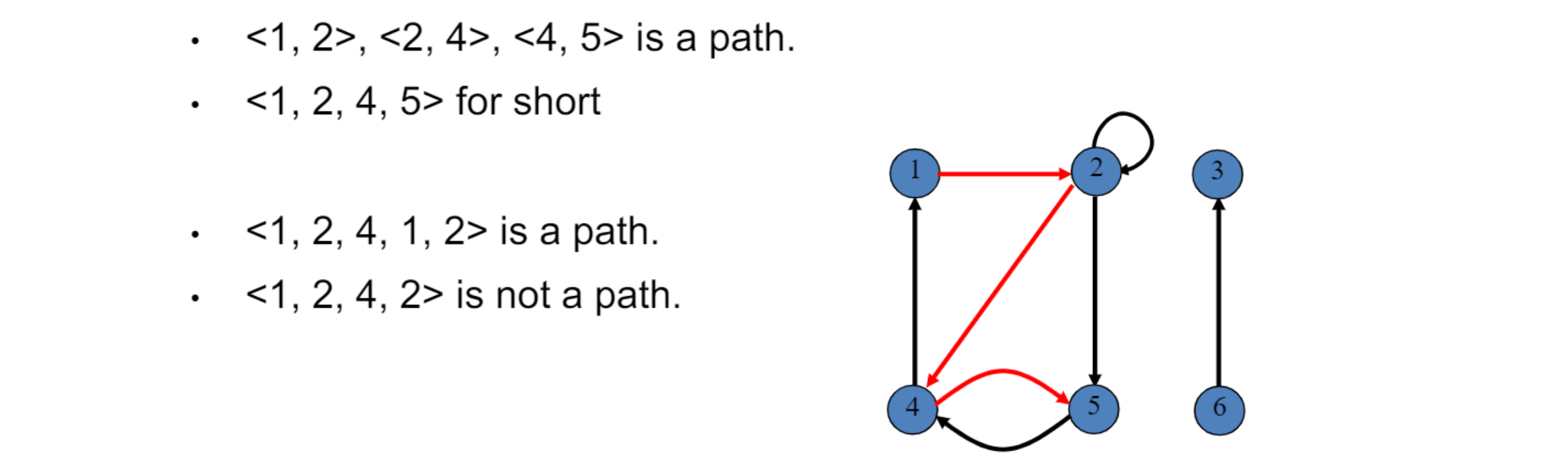
- 또한 path의 length는, path에 있는 edge의 수
- 예를 들어, path <1,2,4,5>의 length는 3
- vertex u에서 v까지 도달하는 path가 있다면, v는 u로부터 reachable 하다고 함.
- 연속적인(consecutive) edge의 sequence
- Simple path
- path의 모든 vertices가 다르다면(distinct) 그 path는 simple하다고 함.
- path <1,2,4,5>는 simple path
- path <1,2,4,1,2>는 simple path가 아님
simple path되려면, 경로 안에 cycle포함 하면 안됨.
- path의 모든 vertices가 다르다면(distinct) 그 path는 simple하다고 함.
- Cycle and simple cycle
- 만약 $v_0=v_k$라면, path $<v_0, v_1, v_2,…, v_k>$는 cycle
- $v_1, v_2,…, v_k$가 distinct 하다면 cycle $<v_0, v_1, v_2,…, v_k>$는 simple
- A path <1, 2, 4, 5, 4, 1>는 a cycle이지만 simple cycle은 아니다.
- A path <1, 2, 4, 1>는 simple cycle
-
An acyclic graph
= cycle 없는 그래프 -
A connected graph
undirected graph가 connect 되어있다
= 모든 pair의 노드가 path로 연결되어 있는 경우 - Connected components
- undirected graph에서 최대로 연결된 vertex의 subset
- undirected graph에서 최대로 연결된 vertex의 subset
- Strongly connected
- 만약 vertex의 모든 pair가 서로서로 reachable 하다면 이때의 direct graph는 strongly connected 하다고 함
- Strongly connected components
- Directly connected graph에서, 최대로(maximally) strongly connected 되어있는 (vertex의) subset
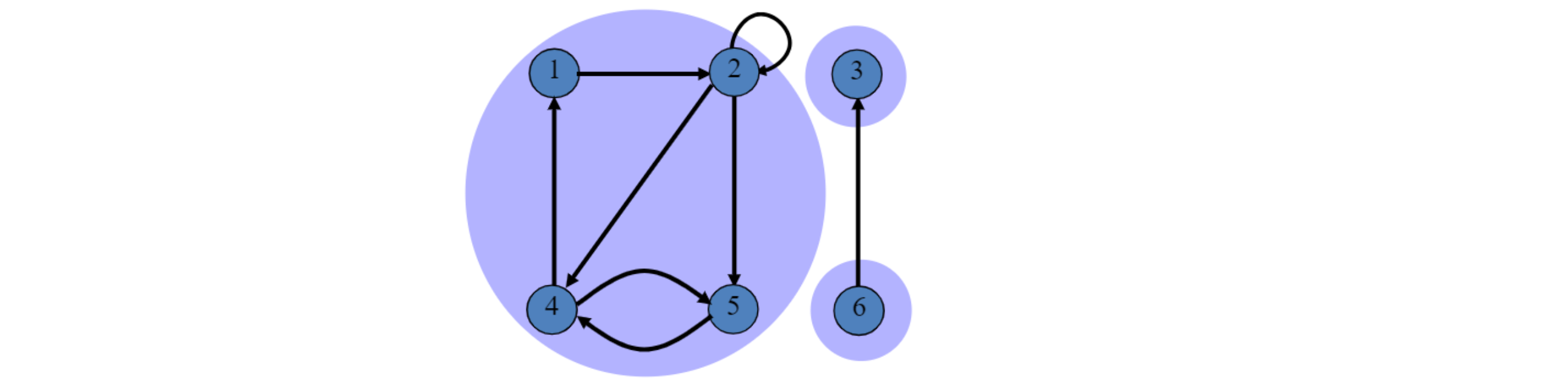
- Directly connected graph에서, 최대로(maximally) strongly connected 되어있는 (vertex의) subset
- A complete graph
- 모든 pair의 vertex가 adjacent한 undirected graph
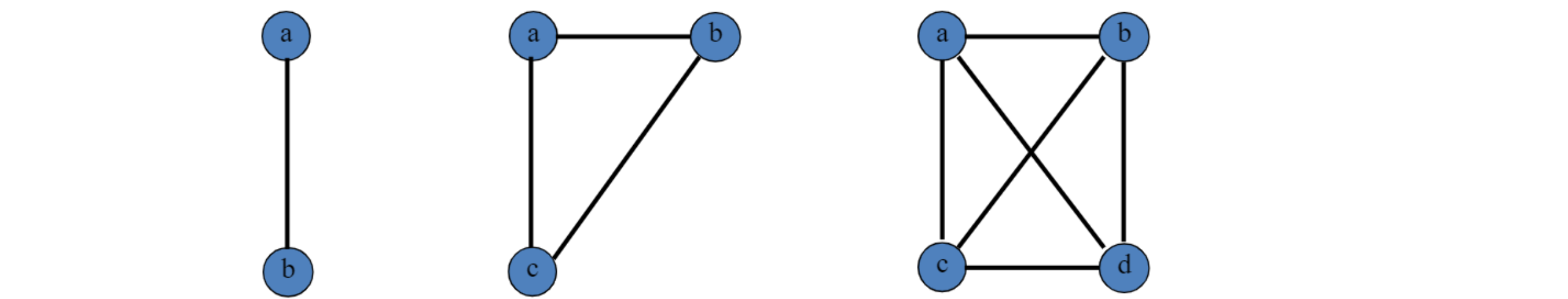
- 모든 pair의 vertex가 adjacent한 undirected graph
- A bipartite graph
- G = (V,E)인 undiredted graph는 두 set $V_1, V_2$로 partition될 수 있고, 모든 edge는 양쪽에 걸침(=동일한 partition에는 edge 없음)
- 그리고 위의 edge조건을 수식으로 표현 하면,
for each edge (u,v), either u∈V1 and v∈V2,or u∈V2 and v∈V1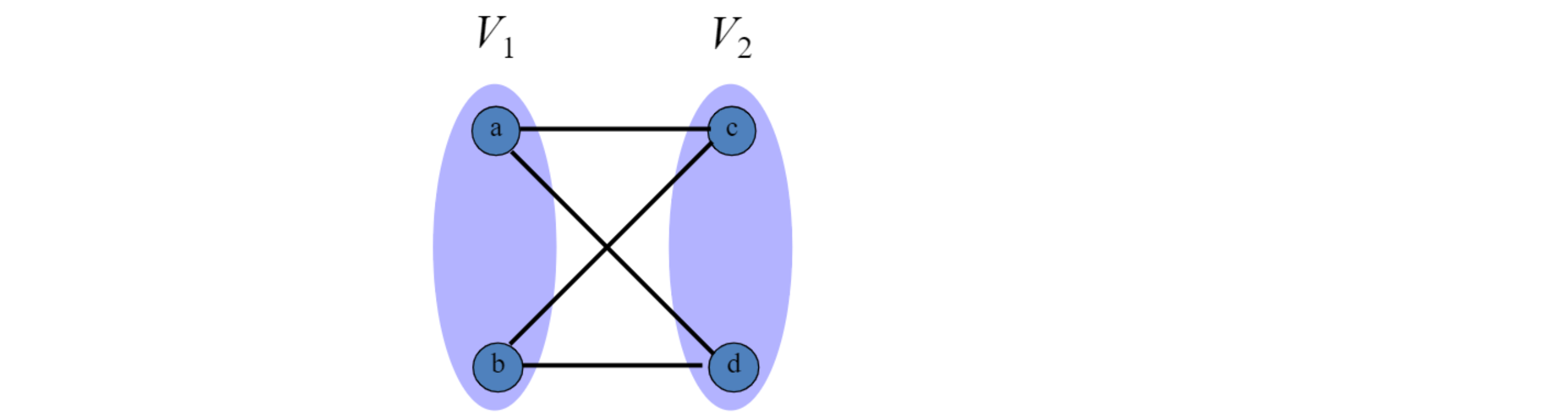
- 그리고 위의 edge조건을 수식으로 표현 하면,
- G = (V,E)인 undiredted graph는 두 set $V_1, V_2$로 partition될 수 있고, 모든 edge는 양쪽에 걸침(=동일한 partition에는 edge 없음)
- Forest
- acyclic, undirected graph
- Tree
- A connected forest
- Tree의 조건: A connected, acyclic, undirected graph
- Root, child 개념 X, 두 node 사이 연결 유무만 의미 O
지금까지 본 tree는 direction 있었음
graph 의 일종으로써 tree는 일반적인 정의로 direction이 없는것. 특별한 경우로써 direction가지는 것 이야기 할것임.
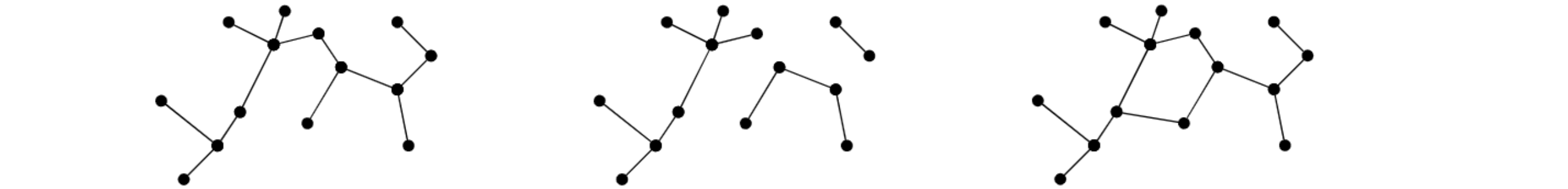
위 그림에서 좌측은 Tree,
중앙은 Forest,
우측은 cycle 있어서 tree X
정리하면, Forest는 tree의 집합
Tree는 forest중에 connected 된 것
- Dag
- Directed acyclic graph
dag로 표현되는 응용 applicaion이 꽤 있음.
이런경우 dag의 특성 이용해 걔산 빠르게 하거나 approximation 하거나… 활용
graph 중 특별한 성질 가지는 것들이 tree, forest, directed acyclic graph 등.
-
Handshaking lemma
if $G=(V,E)$가 undirected graph라면,
$\sum_{v∈V}degree(v)=2|E|$
-> degree와 edge의 개수 사이의 관계 - Tree: connected, acyclic, and undirected graph (좌측은 정의, 하단은 성질)
- 어떠한 vertex도 unique simple path로 연결되어있다
- unique하지 않다면, 반드시 cycle이 생김
- 어떠한 edge라도 제거된 경우, graph는 disconnected된다.
- 특정 edge 지웠는데 그 양끝점 disconnect 되지 않고 연결되어 있다면, cycle이 있었다는 것. $\therefore$ 특정 edge 지우면 disconnect 됨.
- 어떠한 edge라도 추가되는 경우, cycle을 포함하게 된다.
- 추가되는 그 양 끝점 연결하는 unique path가 있었을테니 cycle 생기게 됨.
- |E| = |V| – 1 (node수는 edge수보다 항상 하나 작다)
- 어떠한 vertex도 unique simple path로 연결되어있다
- G is a tree.
= G is a connected, acyclic, and undirected graph
(초기 정의. 아래는 다른말로 표현한 같은 의미 가지는 말들)
= In G, any two vertices are connected by a unique simple path.
= G is connected, and if any edge is removed, the resulting graph is disconnected.
= G is connected, |E| = |V| – 1.
= G is acyclic, |E| = |V| – 1.
= G is acyclic, but if any edge is added, the resulting graph contains a cycle.tree를 정의하는 여러가지 방법
외울필요 없고, 이것 말고 위의 특성알아두면 됨.
✏️ 임의의 두 노드사이에서 unique한 simple path, edge수가 connectiveness 유지하는 최소한의 노드 (cycle 되지 않도록 하는 최대한) -> tree의 이 특성 잊지 말기
- The number of edges(일반적으로 edge와 node의 개수의 관계)
- Directed graph:
$|E| ≤ |V|^2$
$\because$ self loop 까지 포함 하기에 - Undirected graph:
|E| ≤ |V| (|V|–1) / 2
$\because$ self loop 불가하고, 서로 다른 두 node 사이에만 있을 수 있기에
- Directed graph:
Graph representation
그래프의 표현 크게 두가지
- Adjacency-list representation
- Adjacency-matrix representation
Adjacency-list representation
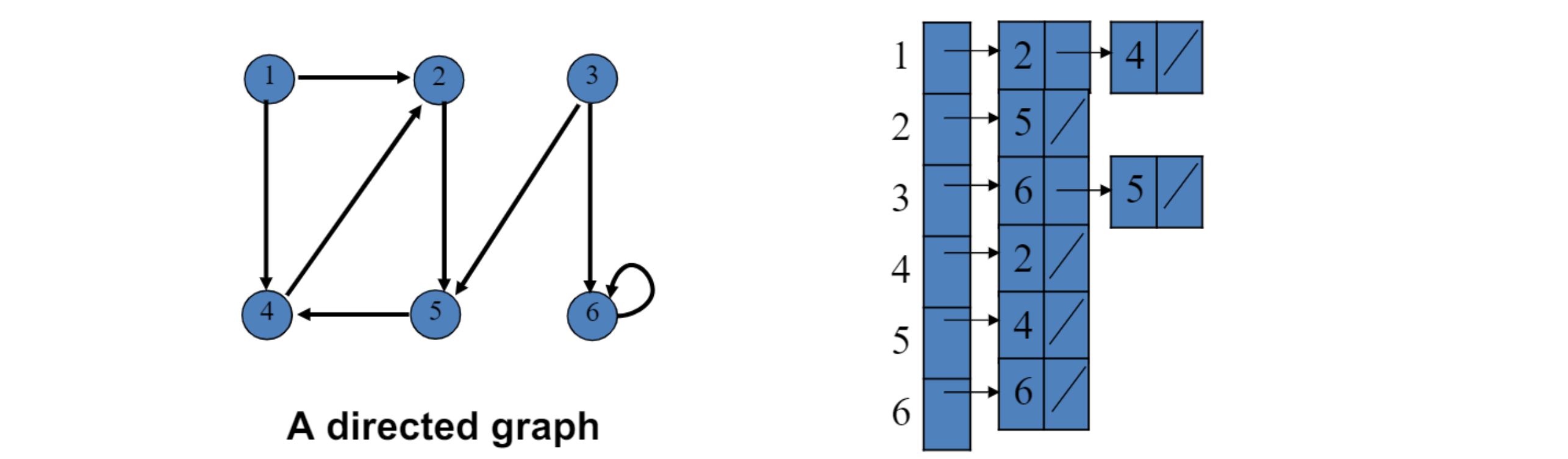 $\vert V\vert$ list에 대한 array.각각이 vertex
$\vert V\vert$ list에 대한 array.각각이 vertex
각 vertex마다 그것의 adjacent들 contain
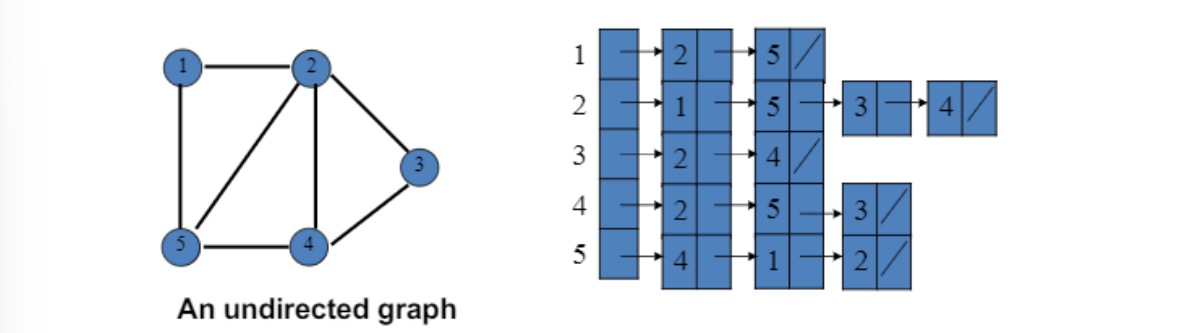 undirected graph의 경우, directed version이 저장됨
undirected graph의 경우, directed version이 저장됨
=> $\theta(V+E)$ space
Adjacency-matrix representation
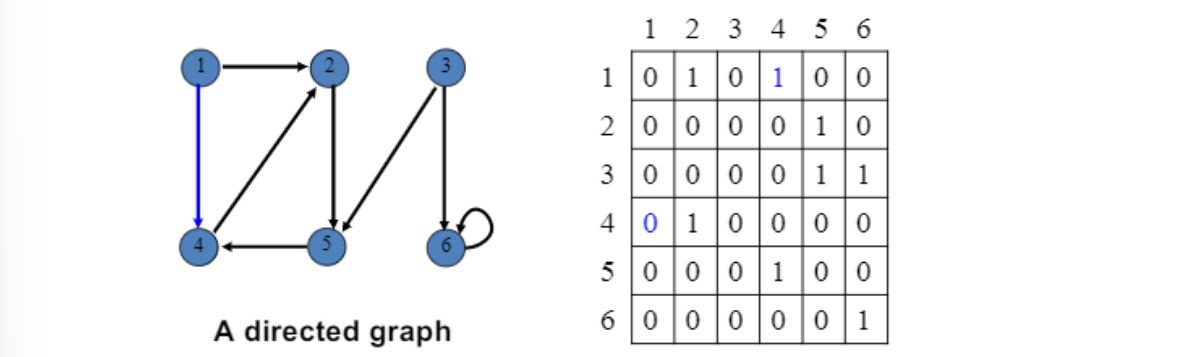
$\vert V\vert \times \vert V\vert$ matrix : $\Theta (V^2)$
Edge가 있으면 Entry$(i,j)$는 1, 없으면 0
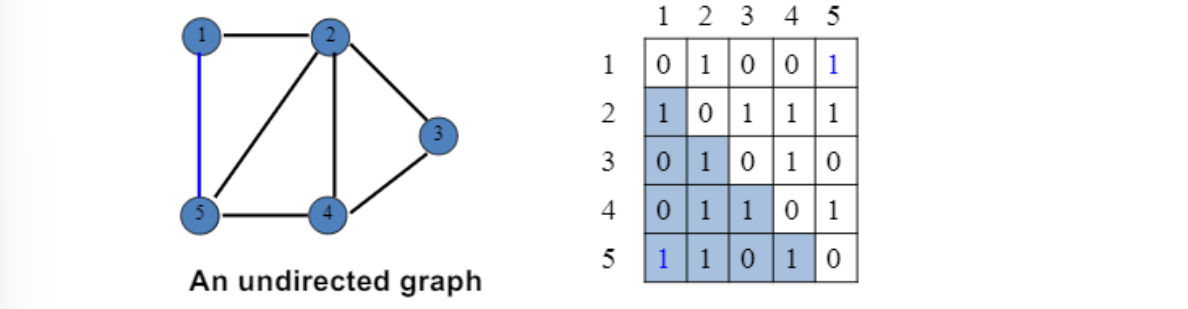
undirected graph의 경우 main diagonal을 따라 대칭
반쪽만 저장하는것도 충분함
Adjacency-list representation, Adjacency-matrix representation 비교
- Storage
- $G$가 sparse 하다면 adjacency list가 나음
$\because \vert E \vert < \vert V\vert ^2$ - $G$가 dense 하다면 adjacency matrix가 더 나음
$\because$ adjancy matrix는 한 entry당 한 bit 사용
- $G$가 sparse 하다면 adjacency list가 나음
- Edge present test : edge $(i,j)$가 존재하는가?
- Adjacency matrix : $\Theta (1)$ time
- Adjacenty list : $O(V)$ time
- Listing or visiting all edges
- Adjacency matrix : $\Theta (V^2)$ time
- Adjacenty list : $O(V+E)$ time
Weight가 있는 Graph인경우
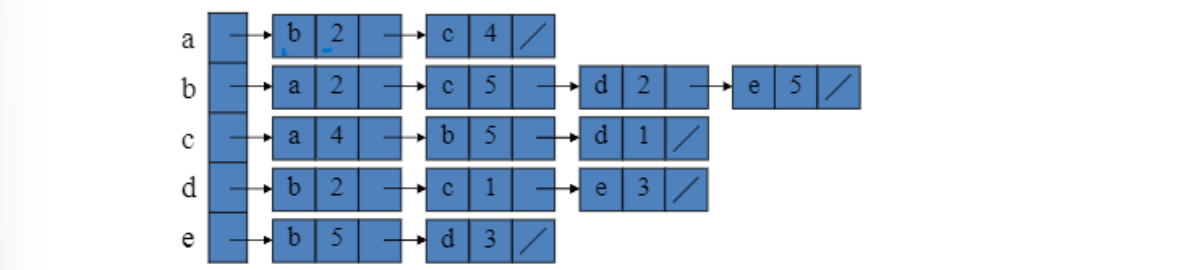 adjacent vertex와 weight를 함께 저장
adjacent vertex와 weight를 함께 저장
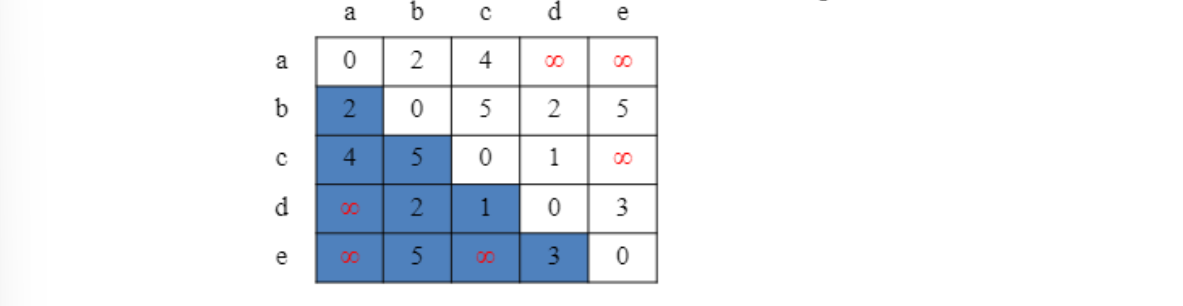 matrix의 각 entry가 weight를 의미
matrix의 각 entry가 weight를 의미
출처 : 2023-2 ITE2039 수업