ITE4005_DS > (8) 5.1 Data analysis and pre-processing part 1
Chapter5, Mining Frequent Patterns, Association and Correlations
[Data Science]2: Getting to Know Your Data part1
데이터의 특성, 데이터 전처리, 유용한 정보 찾기, 분포 등에대해 배움
Contents
- Data Objects and Feature Types
- Basic Statistical Descriptions of Data
- Data Visualization
- Measuring Data Similarity and Dissimilarity
- Summary
Types of Data Sets
- Tabular
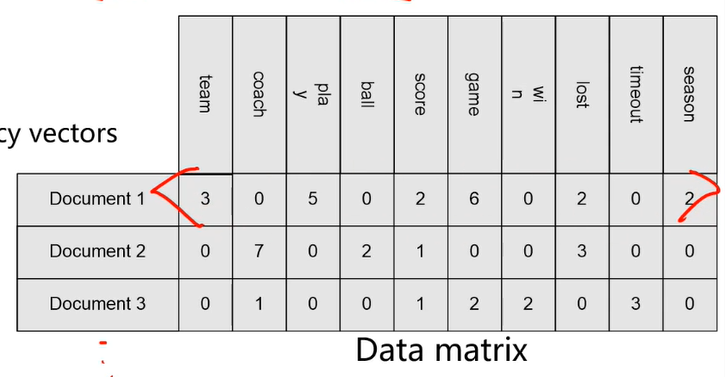
- 각 데이터는 Data matrix / table 로 표현될 수도 있
- 각 숫자가 의미하는 것은 그 단어의 등장 횟수. frequency
- 한 줄은 a set of term-frequency vectors
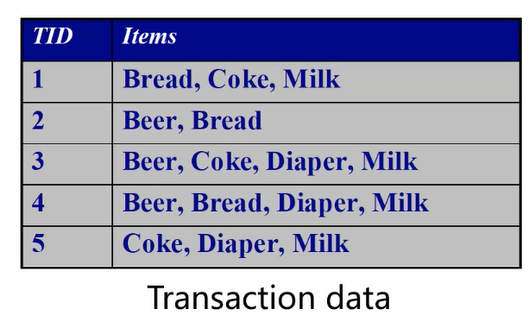
- Transaction data
- Graph and network
- 노드와 엣지로 표현될 수 있는 자료들
- social network
- word wide web
- molecular structures
- Time-series (ordered)
- Video data: sequence of images
- Temporal data: time-series of trajectories (예, 비트코인 가격)
- Sequential data: transaction sequences
- Genetic sequence data
- Spatial, image, and multimodal:
- Spatial data: maps
- Image data
- Multimodal data (video + image + text + ….)
Characteristics of Data
- Dimensionality
- feature의 개수
- 차원의 저주(# of dim이 큰 경우)
- 높은 dimension의 공간인 경우
- 데이터 object 간에 유의미한 정보를 얻는 것이 힘들
데이터 학습을 위한 차원이 증가할 수록 성능이 저하되는 현상
이는 차원이 증가할수록 개별자원 내에 학습할 데이터 수가 적어지는 현상 때문
- Sparsity
-
density 적은 것
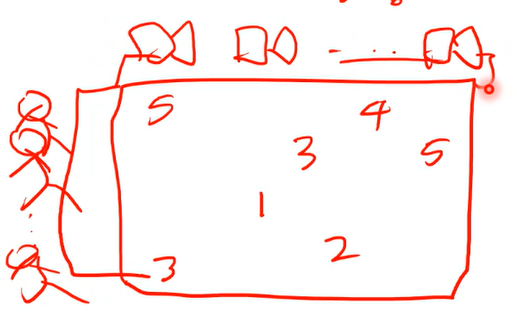
-
위 그림은 rate matrix. 개개인별 영화 점수 준 것인데 대부분의 셀이 비어있음
-
- Resolution
- patterns depend on the scale
- 이미지 데이터에서 데이터 분석 결과는 주어진 이미지의 resolution에 크게 영향
- Distributioin
- Centrality, dispersion
- 평균 등
Data objects
Data set은 data object로 이루어져 있다.
= tuples = samples = examples = instances = data point
DB의 각 row → data object, 각 columns → features
< Features >
- = dimensions = attributes = variables
-
각 data object들의 측정 가능한 property나 특징 (characteristics)
types : nominaly, binary, numeric(= quantative. ratio scaled / interval scaled)
Feature types
- nominal
- 이름 등을 이야기 하는 명사
- 유한한 수의 값
- ex, Hair_color = {black, blond, brown, grey, red, white …}, 결혼 했는지, 직업, …
- Binary
- nominal feature의 특이한 케이스
- ex, 결혼 했다 안했다 2가지
- Symmetric, asymmetric 2가지로 나뉜다.
- Ordinal
- 순서를 가지고 있는 것(ranking)
- ex, Size = {small, medium, large}
- 하지만 각 feature간의 Magnitude(규모)를 알 수는 없다. (magnitude of difference)
- Numeric(integer or real-valued)
- Ratio-scaled
- Ratio(비율)가 의미있다
- 0 없다는 것 의미
- 90kg이 45kg의 두배
- Interval-scaled
- 차이만 의미 있음
- 섭씨 2도가 4도의 절반이라고 할 수 없음
- Ordinal과 다르게 scale 알 수 있음(equal-sized unit 사용하기 때문)
- Ratio-scaled
Basic Statistical Descriptions of Data
데이터를 더 이해하기 위해 central tendency, variation, spread등
Median, max, min, quartiles, outliers, variance, etc.
이들로 각 data의 특징들 represent
-
Mean
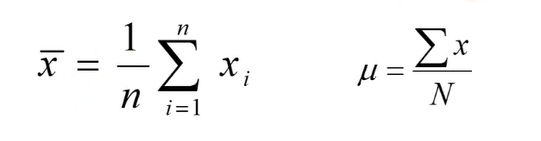
소문자 n은 sample을 의미, 대문자 N은 전체 의미
위 수식의 좌측은 sample의 평균 의미, 우측은 전체 평균 의미
-
weighted arithmetic mean
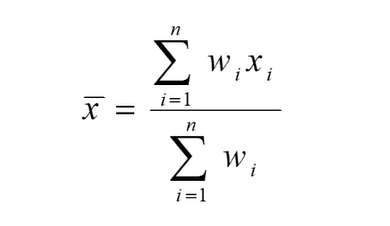
w값에 1 넣어주면 original 버전과 같아짐.
-
Trimmed mean
- feature에 매우 큰 값 있는 경우 필요함(outlier 등)
-
-
Median
위에서 본 mean은 outlier에 크게 영향 받음. Mean은 극단적인 값에 영향 많이 안받음
홀수개 있는경우 가운데 값이고 짝수의 경우 중앙의 두 값을 평균
Sort한 후 중앙값을 찾아야해서 데이터셋이 dynamic(add remove), large 한 경우 어려움(computation issue)
median 빨리 구하기 위한 방법으로 중앙값 추정하는 interpolation 방법이 있음
(새로운 데이터 들어올 때 recomputation. re sorting 할 필요 없음)
계산하는법 차근히 보기
-
Mode
가장 빈번하게 일어나는 값
주로 연속적인 feature가 아닌 discrete features에서 정의됨
mode에서 한 값을 원할 때 → Unimodal, 두 값 → binomial, 세 값 → trimodal
Symmetric vs. Skewed data
다양한 모양의 데이터일 때 median, mean, mode의 위치
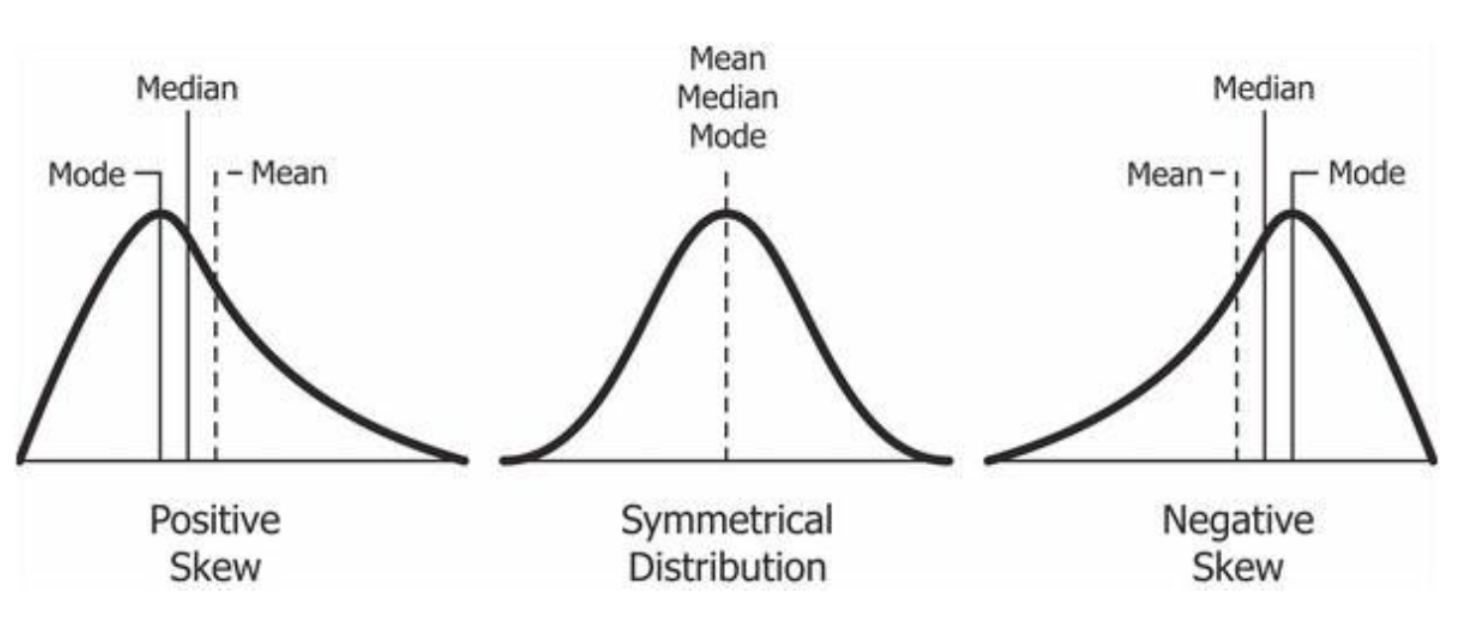
긴 꼬리가 좌측에 있으면 positive skew된 distribution이라고 함
negative skew는 반대
Measuring the dispersion of data
dispartion : data point가 전체 범위에서 어떻게 분포되어있는지
Quartiles, outliers and boxplots
- Quartiles
- Q1 (25th percentile), Q3 (75th percentile)
- Q2는 50%, Q4는 100%를 나타내긴 하지만 1,3번을 자주 씀
- Inter-quartile range (IQR): IQR = Q3 –Q1
- Q3 와 Q1의 범위
- Five number summary: min, Q1, median,Q3, max
- 다섯 개의 수로 roughly dataset의 distribution을 생각할 수 있음
- Box plot
- Five number summary 시각화 한 것
- 대략적인 분포 알 수 있
- Outlier
- 다양한 정의 및 방법이 있지만, IQR의 1.5보다 작거나 클 때 outlier 라고 하는 방법 있
box plot 디테일
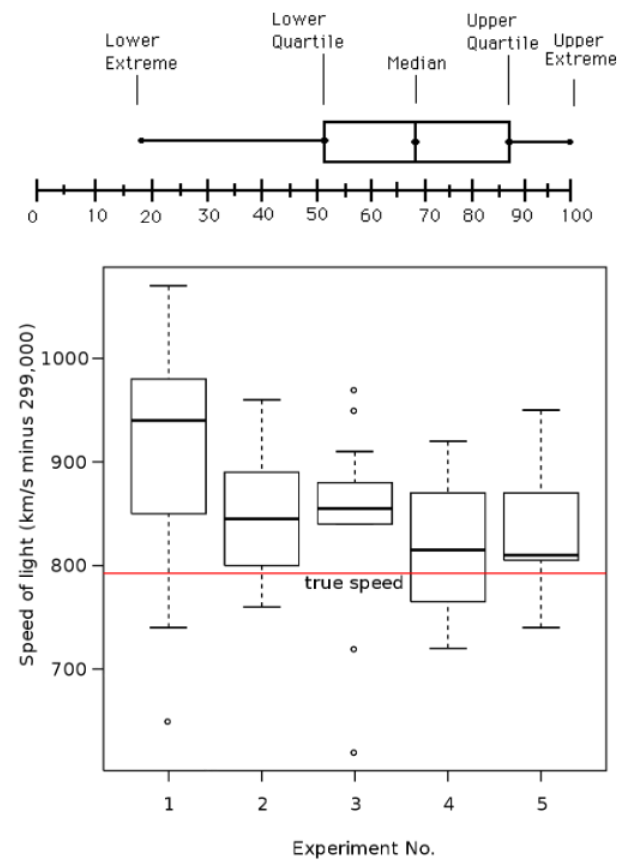
- 박스의 범위는 Q1과 Q3 사이.
- 박스 안의 선은 평균을 의미
- whiskers : 박스 밖의 두 선은 minimum 값과 maximum 값
- Outliers: 작은 원으로 individually 표현 된 것
Variance and standard deviation (sample:s, population: σ)
- variance
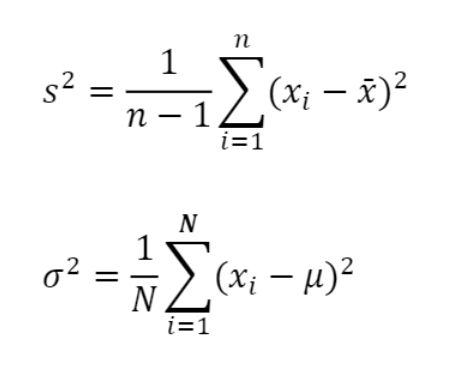
- standard deviation
- variance의 square root
데이터의 dispersion을 측정하는 다른 방법은
Normal distribution property 사용
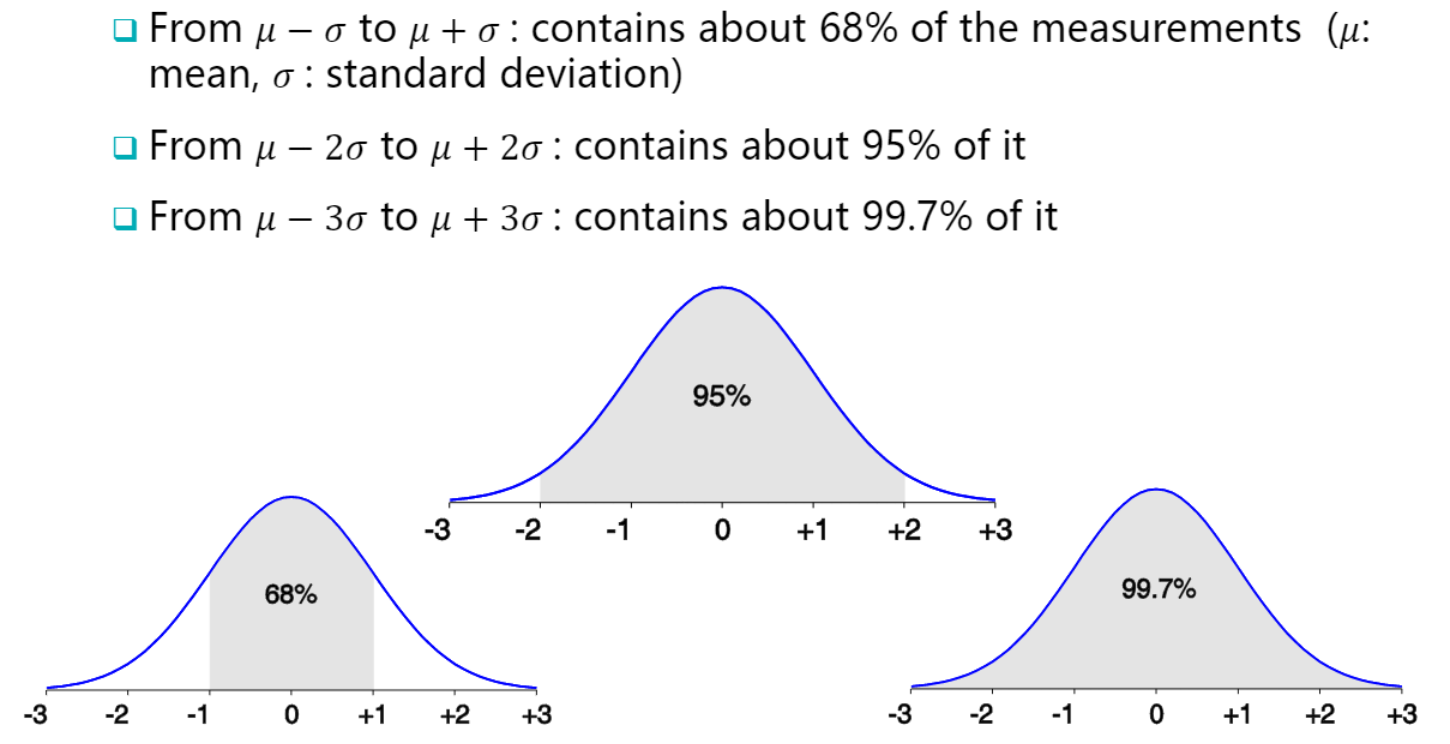
이걸 사용해서 어떻게 대략적인 분포?
출처 : 2023-1 ITE4005 수업